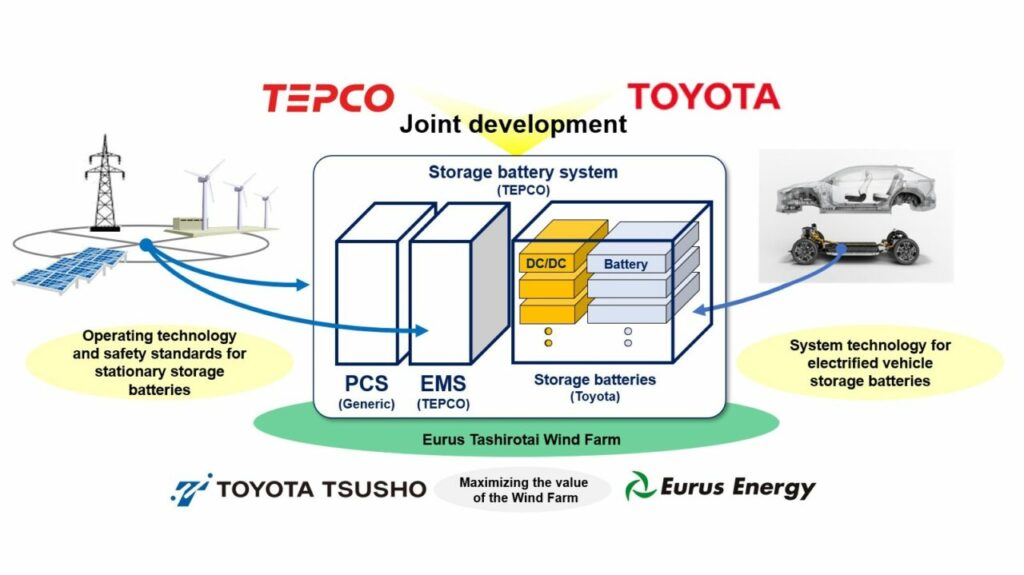
A battery storage system made with second life EV batteries has been developed by carmaker Toyota and Japanese utility company Tokyo Electric Power (TEPCO).
The battery energy storage system (BESS) has been developed ahead of anticipated increases in global market demand for the technology, and will be installed at a wind farm in Japan where its operation and performance under real-world conditions will be evaluated.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
The 1MW/3MWh BESS uses technology developed by Toyota specifically for controlling electric vehicle (EV) batteries as stationary storage units, and operating technology and safety standards developed by TEPCO.
Toyota said in a release that it expects the verification project to begin construction “around summer” this year, with verification tests to begin before the end of 2023.
Toyota and TEPCO aim to use the project towards the development of storage systems for consumer energy services applications such as backup and integrating onsite renewables generation, and balancing the supply and demand of electricity on the grid as the share of renewable energy grows.
The pair’s new BESS solution can be connected with power conversion systems (PCS) that exist on the market already today, and use multiple stacked battery units.
While details of where battery cells will come from for the installation were not given, Toyota Motors said it will work with two other companies in the Toyota Group, infrastructure and industrial development solutions company Toyota Tsusho and machinery manufacturer Toyota Industries, as well as automotive OEM Denso – in which Toyota has a 25% stake – in its second life repurposing activities.
The company said that evaluation of the new second life BESS will be conducted “over the next several years of operation”, at Eurus Energy Holdings Corporation’s (Eurus Energy’s) Tashirotai Wind Farm, a 7.650MW renewable energy power plant that itself went into operation in 2002.
Eurus Energy and its parent company – Toyota Tsusho – will carry out the installation, with Toyota, TEPCO, Eurus and Toyota Tsuho all playing an active role in the battery storage verification project.

Toyota Tsusho is also known to be working on a US project to trial the use of zinc-air batteries made by startup E-Zinc to provide 24-hour long-duration energy storage (LDES) at another Eurus Energy wind farm, this time in Texas.
In an interview with this site in April, E-Zinc CCO and US country manager Balki Iyer said that project had been pushed back a little from its Spring 2023 anticipated start date, but that the companies involved were “largely on track with the project timeline”.
Eurus also began its own first BESS project late last year, a 1.5MW/4.85MWh installation in Fukuoka, southern Japan, aiming to use it for participation in power trading markets and grid-balancing.
In perhaps more closely related news, in late October last year, Toyota Motors and Japanese power generation group JERA (a joint venture between TEPCO and another utility, Chubu Electric Power) partnered to develop and deploy a hybrid BESS combining three types of battery.
Also using batteries “reclaimed” from EVs, that project, at a thermal power plant in Japan’s Mie Prefecture will feature a 485kW/1,260kWh system that comprises lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride and lead-acid batteries.
In an earlier tie-up, from 2019, Toyota and TEPCO were among partners developing and trialling a bi-directional energy trading system using blockchain ledger technology in the pair’s homeland, while Toyota Tsusho more recently was involved in a project in Japan that got approval to supply vehicle-to-grid (V2G) energy into grid-balancing power markets.
Read more of Energy-Storage.news’ coverage of the second life BESS space, here.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 1st Energy Storage Summit Asia, 11-12 July 2023 in Singapore. The event will help give clarity on this nascent, yet quickly growing market, bringing together a community of credible independent generators, policymakers, banks, funds, off-takers and technology providers. For more information, go to the website.






