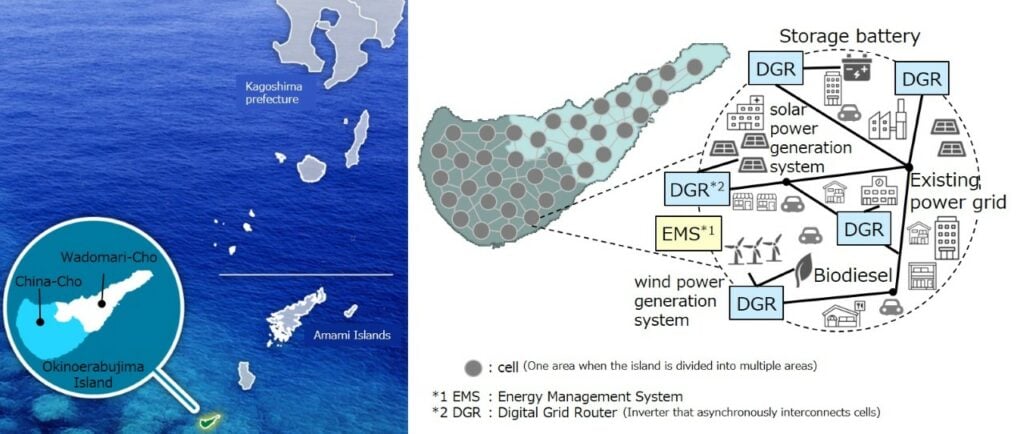
A tiny, coral reef-surrounded island in southern Japan will be able to use renewable energy as its main source of power, thanks to a microgrid with battery storage technology at its heart.
Technology company Kyocera has entered a partnership agreement to build the microgrid with municipal governments of China-cho and Wadomari-cho, which are the two towns on Okinoerabujima, an island less than 100km2 in area and with a population of about 12,000 people.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
The island, about 2,000km south of Tokyo, has a subtropical climate and is prone to typhoons, which cause frequent power outages. Both of its towns are reliant on imported diesel for electricity and in addition to the logistical difficulties and costs of bringing the fuel in, keep the region locked into a cycle of high greenhouse gas emissions.
Kyocera’s project is being supported by subsidies from the central government of Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) for promoting local cooperation through the use of renewable energy.
It will combine solar PV, wind turbines, battery energy storage and an energy management system (EMS) to balance supply and demand. No new power lines will be required, said Kyocera, which itself makes key equipment of the type that will be used, including battery storage and solar PV modules.
Kyocera told Energy-Storage.news that the sizing of the system or its components have not yet been determined for the project, which is at an early stage. Feasibility studies are underway and plans are expected to be created by March next year, with construction activities including installation of solar, batteries and EMS equipment to begin in April.
The company did say that the scale of electricity demand on the island is more than 10MW, and that “tens of megawatts” of solar power, wind, and “tens of megawatt-hours of storage batteries and electric vehicles are needed to decarbonise this island”.
“Details of this entire system are being discussed,” Kyocera said.
The company plans to build a small-scale microgrid system centred on public facilities, which have several hundred kilowatts demand. The microgrid will have “hundreds of kilowatts of solar power… and hundreds of kilowatt-hours of battery storage,” the company said.
“CO2 emissions from the power sector in the area will be virtually zero.”
As well as managing and integrating power from variable solar and wind sources, the microgrid will give the region resilient power during emergencies and natural disasters. Under the project agreement, Kyocera and China-cho and Wadomari-cho will create a local power company to maintain the facilities.
China-cho declared a climate emergency in September 2020, joining a handful of other Japanese local authorities to do so since the government of Nagano Prefecture in the north of the main Japanese island of Honshu was the first in 2019.
Last week, Energy-Storage.news reported that the installation of a 15.6MWh battery energy storage system (BESS) on the Portuguese island of Madeira will allow that region to source about 50% of its energy from renewables.






