
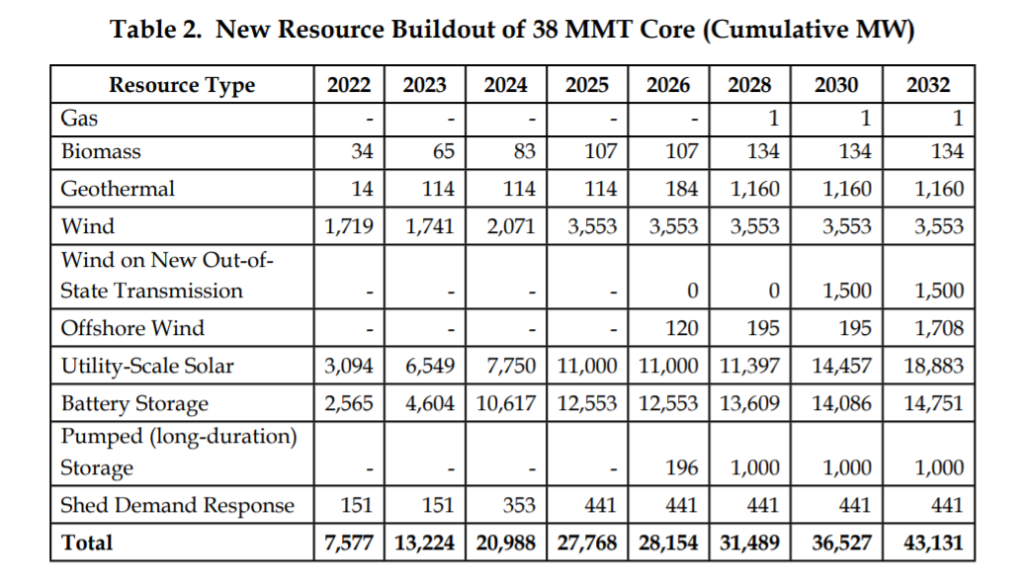
The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) has unanimously approved plans to add more than 25.5GW of renewables and 15GW of storage in the state by 2032 at a cost of US$49 billion.
Approved last week (10 February) by the CPUC, the plans will see the state add 18,883MW of utility-scale solar, around 6,700MW of wind power, 14,751MW of battery energy storage systems (BESS) and 1,000MW of demand response resources.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Taken together, these resources would cost US$49.3 billion and would produce a levelised cost of energy of US$18.6c/kWh in California.
The plan adopted a 35 million metric ton (MMT) 2032 electric sector GHG planning target (38 MMT by 2030), which is more stringent than the 46 MMT GHG target that was adopted previously. If realised, it would see renewable resources account for 73% of the state’s energy mix by 2032.
“Today’s decision provides direction for procurement of an unprecedented amount of new clean energy resources. It keeps us on the path toward achieving our state’s ambitious clean energy targets, while ensuring system reliability,” said CPUC commissioner Clifford Rechtschaffen.
The CPUC said a preliminary analysis indicates there is “sufficient space for all of these new resources on the existing transmission system, with only limited transmission upgrades needed by 2032”, adding that utility-scale battery storage projects were identified as alternatives to transmission upgrades at a lower cost to ratepayers.
“This finding will be validated at a more granular level by the California Independent System Operator (CAISO) in its 2022-2023 Transmission Planning Process (TPP),” CPUC said.
At the start of this month, however, CAISO released a report, which CPUC was involved in making, that said the state would need a US$30.5 billion investment in its transmission system to accommodate the expected 53GW of solar PV that will exist on its network by 2045.
Around the same time, the CPUC decided to indefinitely delay its decision on controversial changes to the state’s net metering laws after widespread criticism of the plans, dubbed NEM 3.0.
Research organisation Wood Mackenzie warned the changes, proposed by the CPUC in December 2021, would severely reduce residential PV’s value proposition in California, cutting its solar market in half by 2024.
This story first appeared on PV Tech.






