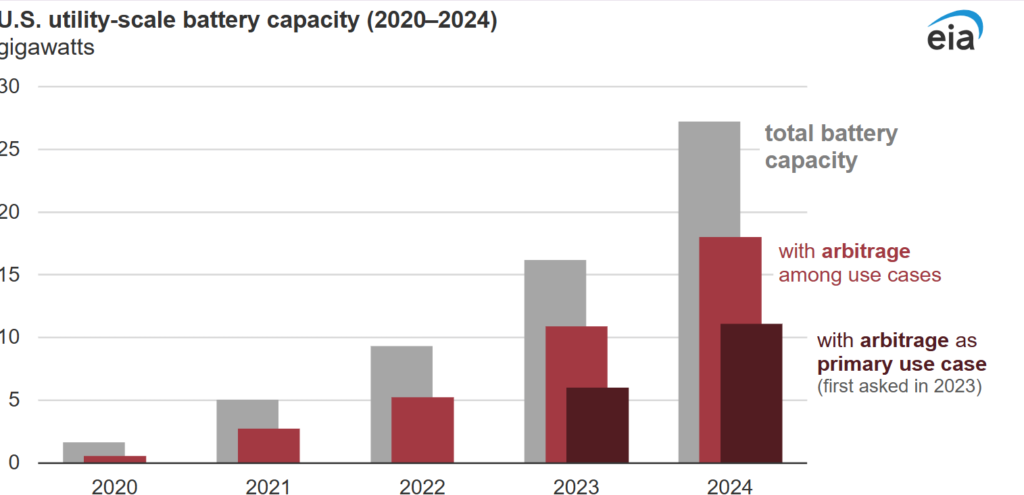
The US Energy Information Administration (US EIA) annual survey of power plant activity found that in 2024, utility-scale batteries were more commonly used for price arbitrage.
From the US EIA, “66% of all utility-scale battery capacity had arbitrage among its uses, and that 41% of the total capacity was primarily used for arbitrage.”
The US EIA was formed by the Department of Energy in 1977, and by law, operates independently of policy considerations.
Stephen Nalley is the acting administrator of the EIA. Donald Trump’s pick to lead the administration, Tristan Abbey, was confirmed by the US Senate on 18 September but has not yet taken over as administrator.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
The survey, Form EIA-860 gathers detailed information at the generator level about existing and planned electric power plants, including associated environmental equipment, for facilities with a combined nameplate capacity of 1MW or more.
Starting in 2023, EIA began asking operators to identify the primary use case for their battery system.
In the 2023 survey, operators utilised about 11GW of capacity for arbitrage out of the total 16GW recorded. Of this 11GW, roughly 6GW was primarily dedicated to arbitrage activities.
In 2024, the total capacity was around 27GW. Of this, about 18GW was utilised for arbitrage, with an estimated 11GW mainly dedicated to this purpose.
The primary use cases during that year, ordered from greatest to least common, were arbitrage, frequency regulation, excess wins and solar generation, system peak shaving, load management, co-located renewable firming, ramping/spinning reserve, load following and voltage or reactive power support.
Arbitrage led over frequency regulation by approximately 4.5GW, and frequency regulation meanwhile, led over excess wind and solar generation by about 3GW.
As explained by EIA, “frequency regulation was the primary usage for 24% of battery capacity. In previous years, operators had reported that frequency regulation was the most common use case for their battery systems.”
By the end of 2024, the California Independent System Operator (CAISO) reported a total of 11.7GW of battery capacity, with 43% mainly dedicated to arbitrage.
The Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) reported 8.1GW of battery capacity, with half mainly used for arbitrage.
Arbitrage strategies have had to become more complex. As Ali Karimian and Alden Phinney of GridBeyond explained in a guest blog for Energy-Storage.news:
“While ancillary services-focused approaches delivered solid returns in ERCOT during 2023, and basic charge low/discharge-high strategies worked effectively in CAISO, the rapid deployment of BESS assets has created intense competition, which demands sophisticated optimisation to capture excess returns beyond market benchmarks.”
Karimian and Phinney continued, “To remain competitive, battery storage operators must transition from basic arbitrage strategies to highly optimised, integrated solutions that capture returns that outperform the benchmark when adjusted for risk (what the financial world calls alpha).”
EIA says the early release 2025 data for Form EIA-860 is scheduled for June 2026. As the markets in ERCOT and CAISO evolve, it will be interesting to observe what operators report to EIA as compared to 2023 and 2024.





