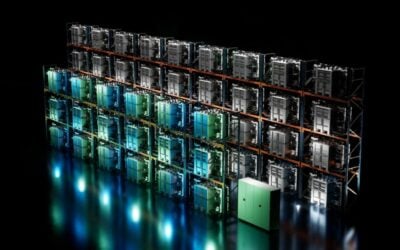
RES’ ‘Elwood’ large-scale storage system in Chicago. Image: RES Group.
The signing of a contract to deploy batteries for dynamic frequency response in Britain is an indication that grid operators and the renewables industry can work together to benefit energy users, developer RES has said.
National Grid, sole operator of Britain’s electricity transmission system, has contracted RES Renewable Energy Systems to install 20MW of energy storage for dynamic frequency response on its networks. This stands separately to National Grid’s much-anticipated 200MW tender for another form of grid-balancing, enhanced frequency response (EFR), which is taking place over the summer.
John Prendergast, manager for energy storage at RES, told Energy-Storage.News that the project was proposed to National Grid by the company in 2014. According to Prendergast, this was based on RES’ experiences of delivering “multiple similar projects in the US”. National Grid and RES have signed a four-year contract for the service.
“We undertook a significant amount of detailed technical analysis on the benefit of such a service to the GB (Great British) electricity system, and worked closely with National Grid in testing and proving National Grid’s own analysis of the value of very fast frequency response services,” Prendergast said.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
“This contract therefore stands as an example of how National Grid and renewable energy leaders like RES can work together to deliver innovative new services to assist grid balancing, ultimately to the benefit of GB energy users; domestic and commercial.”
Out of a total of over 100MW and 60MWh of energy storage RES has installed across a number of markets including the US and Canada, a number of these projects have been in the service area of PJM Interconnection, considered the most attractive market to have implemented the Federal Energy Regulation Commission (FERC) Order 755, which allows fast-acting energy storage resources to play into the frequency regulation market.
While both forms of frequency response require fast response to grid signals, dynamic frequency response is provided continuously to the network to manage second by second changes on the system, while enhanced frequency response sees power put into or taken out of the grid to keep frequency close to its optimum (50Hz in the case of the UK). Systems providing EFR must respond to a grid signal within one second or less of registering a frequency deviation.
In addition to the latest deal for National Grid’s transmission network, RES also recently signed what it claimed was the first “fully wrapped” contract to build a UK energy storage facility for a distribution network operator (DNO).
Britain’s energy trilemma
The UK’s government Department of Energy and Climate Change (DECC) is currently facing a number of challenges in setting its future energy strategies. When recently questioned over delays and allegedly spiralling costs at the planned Hinkley nuclear power station, minister Andrea Leadsom restated her department’s three guiding principles in order of priority: to guarantee energy security, to do so at low cost to taxpayers and to decarbonise.
Roberto Moreira, an expert at a London university, Imperial College, recently told Energy-Storage.News that if regarded as a “trilemma” facing the UK, in which the three priorities were to be given equal weight, energy storage as a technology would be appropriate for meeting each of these challenges.
RES’ John Prendergast gave his take on that message.
“Greater flexibility and speed in grid balancing, through services such as this, will allow increased penetration of renewable energy generation onto the GB (Great British) grid,” he said.
“This presents an additional benefit to GB consumers as renewables – particularly the lowest cost technologies such as onshore wind and solar – are becoming established as the cheapest form of all new electricity generation.”
Executing energy storage projects, while different in terms of the business models and structures through which they are financed, could be a very “natural fit” for renewables developers such as RES from a technical standpoint, Dean Frankel, analyst at Lux Research, told Energy-Storage.News (then PV Tech Storage) in November 2014 as RES executed one of its first major projects in the US.
Minister Andrea Leadsom and others appear to rank the UK’s three serious challenges in energy in order of importance.