
The first ‘smart neighbourhood’ in the US state of Georgia is being created by utility Georgia Power and homebuilder PulteGroup, with each home equipped with solar PV, battery energy storage and other smart, clean and distributed energy resources.
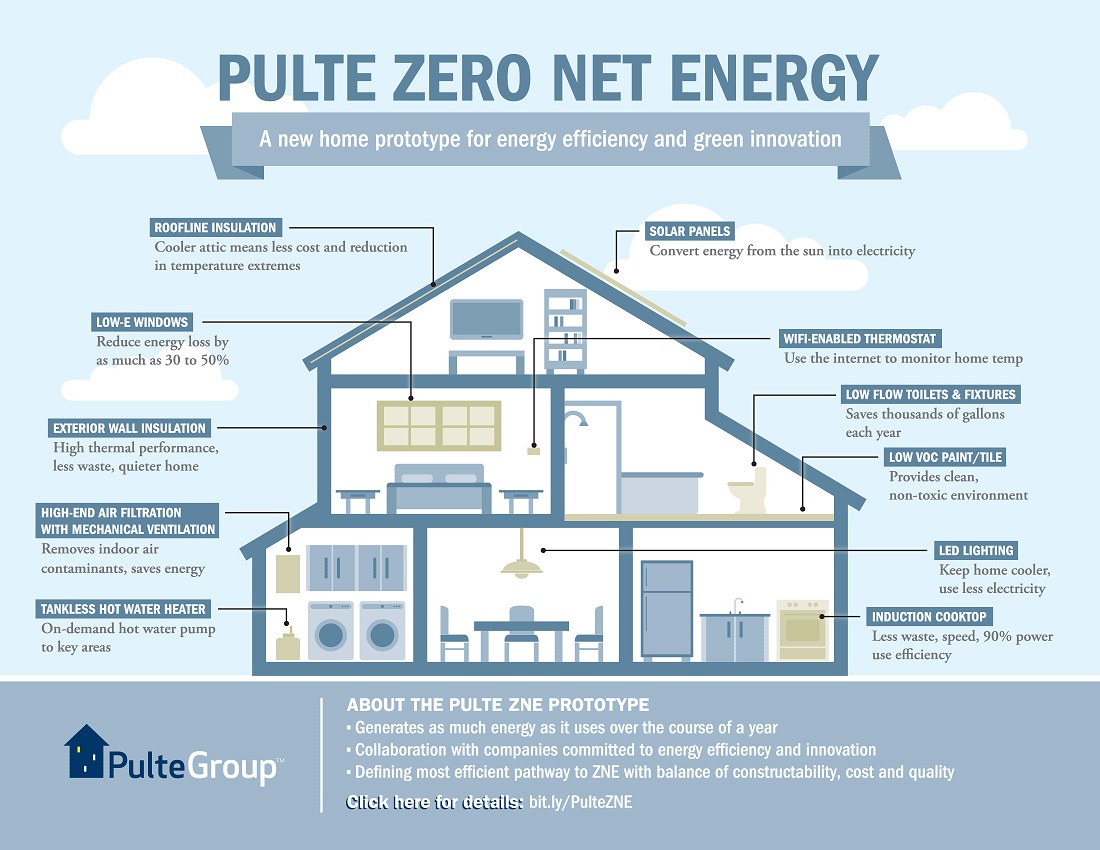
PulteGroup said the planned new development builds on learnings from a prototype Zero Net Home, a residential building which offsets total energy consumption, either through efficiency measures or by producing more clean energy than the amount drawn from conventional grid sources. That prototype was built in northern California for local investor-owned utility Pacific Gas & Electric’s (PG&E) Zero Net Energy Production Builder Demonstration scheme, in a state which has already mandated new residential dwellings to be net zero energy by 2020.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Georgia Power, a subsidiary of Southern Company, will use Georgia Power Smart Neighbourhood as a real-world R&D and test facility for the future of such homes, much in the same way as Panasonic’s Fujisawa Sustainable Smart Town project in Japan has been doing since opening in 2014.
An initial 46 homes are planned at the Georgia development, each with 3 or 4 bedrooms, equipped with modern insulation, advanced heating and cooling, LED lighting and home automation including smart thermostats and voice-activated controls.
Through this partnership with Georgia Power, we continue to be at the forefront of energy efficiency that can shrink our homes’ carbon footprint, but also make our homes less expensive to own, translating into lasting savings for homeowners,” Ryan Marshall, president and CEO of PulteGroup said.
The development is planned for a grand opening later this year.
PV and energy storage players aim for zero energy home future
Neither party has yet revealed which equipment suppliers will be kitting out the homes with PV, energy storage and related management and control platforms. To date, several big players in PV have begun producing systems for new houses with prominent examples being SunPower, which has tie-ups with vendors of ready-built homes in the US and Japanese thin-film manufacturer Solar Frontier, which has tie-ins with Sekisui House, a major house-builder in its home country. In the latter case, Japan’s industry is likely to target the sector aggressively as, like California, there is a policy in place for new homes to be designed and built to net zero energy standards by 2020.
Perhaps the biggest single development of this type is the recent project by Sonnen with Mandalay Homes in Arizona, where 3,000 new residences will be fitted with the German company’s energy storage systems. While not ‘zero energy’ as such, the combination of batteries and on-site solar generation are designed to give the community “very low” power bills “from the outset”, Sonnen said, and the 3,000 battery systems aggregated together will form a “virtual power plant” resource with a 23MWh capacity for an output of 11.6MW.






