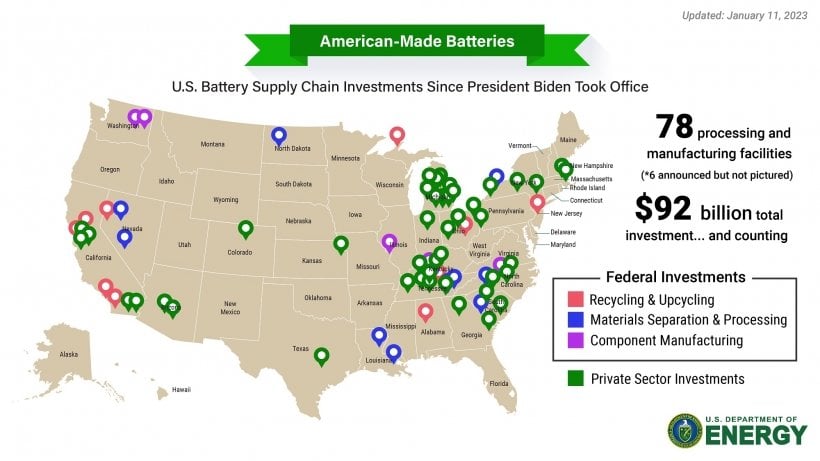
A total of US$92 billion has been invested in the US battery supply chain since President Joe Biden took office in January 2021, including recent projects announced by ICL and Rhyolite.
The figure includes government and private sector investments into the country’s battery supply chain, including recycling, materials separation and processing and component manufacturing. A total of 78 facilities have been announced, with 72 of them pictured in the above infographic.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
One of those is Israel-based speciality minerals firm ICL’s LFP cathode material plant in St Louis, Missouri, previously reported on by Energy-Storage.news late last year, which ICL re-reported to Japanese and Korean markets this week.
The US$400 million project will be half-funded by a grant from the federal government through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law’s US$2.8 billion funding for battery projects, though this still needs to be finalised with the Department of Energy (DOE).
ICL said that by 2025, the share of LFP batteries is expected to reach 30% of all battery shipments by 2025, driven by increased adoption in the EV space as well as growth in energy storage and EV charging infrastructure, two sectors increasingly opting for LFP chemistry ahead of nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC).
Research firm Wood Mackenzie Power & Renewables said in early 2022 that it expected that LFP will be the dominant battery chemistry over NMC by 2030, as previously reported by Energy-Storage.news.
Earlier in the month, the DOE’s Loan Programs Office, headed by industry veteran Jigar Shah, announced a conditional commitment to provide a US$700 million loan for an upstream lithium project. The Rholite Ridge project in Esmerelda County, Nevada, would process lithium carbonate which would provide the needed material for around 370,000 EVs a year.
The Inflation Reduction Act increased the LPO’s loan authority from US$60 billion to US$100 billion. The institution offers interest rates at US treasury levels and also has a longer tenor (repayment period) than a commercial bank, at 10-15 years versus just a few years for the latter.
As Energy-Storage.news has reported extensively, the Inflation Reduction Act and its precursor the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law have seen the investment climate around the US battery supply chain improve substantially.
Within the lithium-ion gigafactory space, this has been illustrated by the US’ planned capacity growing twice as fast as Europe’s since the Act was passed in August. Companies working in project site selection and development recently told us that companies have been pivoting interest westwards across the Atlantic in light of the incentives and support provided by the two schemes.
This has led Europe to announce plans for its own Inflation Reduction Act-style package of support measures to prevent a potential outflow of investment from its battery ecosystem, a concern recently raised by policymakers.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 5th Energy Storage Summit USA, 28-29 March 2023 in Austin, Texas. Featuring a packed programme of panels, presentations and fireside chats from industry leaders focusing on accelerating the market for energy storage across the country. For more information, go to the website.






