Microgrid simulation facilities at universities in Germany and Australia are being supplied with technical solutions by major global power equipment and systems providers AEG Power Solutions and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
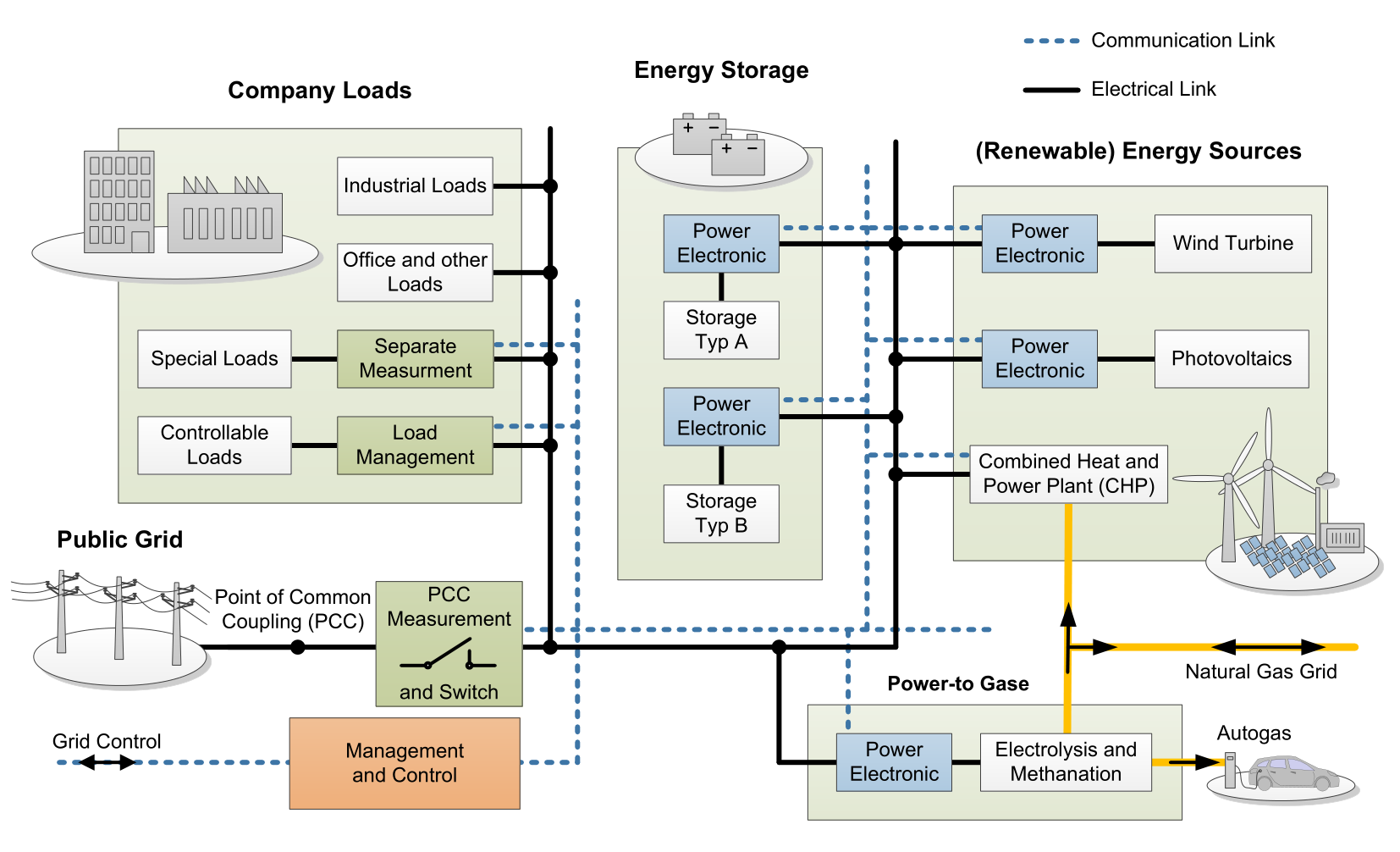
The University of Paderborn in northern Germany has a new microgrid laboratory which can emulate the behaviour of self-contained power systems using resources such as solar panels and wind turbines paired with battery storage and other components like combined hear and power plants.
The facility will be able to emulate up to 16 energy system components which can act as power source or consumer, which acts as a flexible and modular development and validation platform to test how different electrical grids behave under different conditions. Each power node of the emulator will be able to convert distributed energy resources of up to 250kVA.
The EU’s European Regional Development Fund helped pay for the project, along with the local Northrhine-Westphalia government and the university itself. AEG Power Solutions was selected to provide power electronics including its Convert SC Flex energy storage power converter, which in this project will be used to connect the emulator facility to the public electricity grid.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
Coincidentally, also this week Hitachi ABB Power Grids donated a Microgrid Control Systems Testing Facility to Charles Darwin University in Australia’s Northern Territory.
The simulator was built by Hitachi ABB Power Grids to “simulate and troubleshoot” issues in the region’s power network, the company said, such as how to integrate growing amounts of solar energy into the grid and how to island – or separate – parts of the grid to run on local electricity resources when the rest of the grid experienced problems.
“The major challenge in achieving a high proportion of renewable energy (especially solar PV) in power grids is the instability and unreliability of the grid due to the intermittent and hard-to-predict nature of the renewable sources,” Charles Darwin University’s Professor Shuresh Thennadil said.
“In order to achieve the 50% Northern Territory Government target and progress further to net zero emissions, it is essential to develop innovative methods that can deliver safe and stable operation of high-penetration renewable energy grids. Using this facility, we can conduct scenario-testing of an energy system from anywhere in the world.”
In a recent interview with Energy-Storage.news, Maxine Ghavi, Hitachi ABB Power Grids head of Grid Edge Solutions, spoke about how lessons learned from integrating renewables while keeping power stable in remote parts of grid-connected Australia and elsewhere are increasingly being applied in a wide range of localities and scenarios.