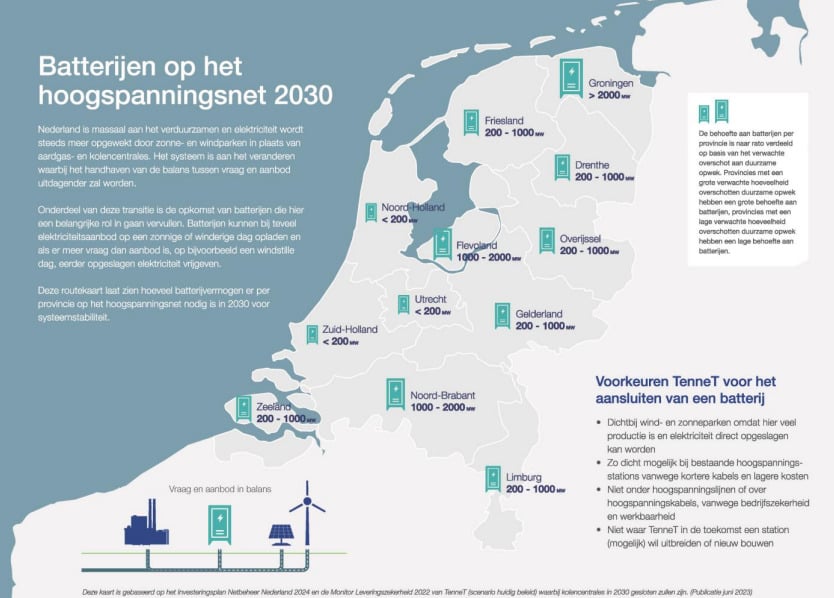
Dutch transmission system operator (TSO) TenneT says the Netherlands will need 9GW of large-scale battery energy storage system (BESS) capacity connected to its grid by 2030.
TenneT said it faces several near-term challenges on its electricity network which BESS projects of 70MW-500MW in size could help alleviate. Grid volatility in terms of frequency, inertia and voltage will rise due to an increasing mix of wind and solar.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Large-scale BESS could also help with the transport of power across the grid through upward and downward dispatch, TenneT said in its corporate presentation which you can read here.
It could also provide balancing through FFR (fast frequency response) and FCR (frequency containment reserve), as well as inertia and reactive power products.
The grid-scale energy storage in the Netherlands market has yet to take off with regulatory challenges the main barrier according to one developer interviewed earlier this year. One of the country’s main utilities Eneco recently called for more action from its own government as it announced a 200MWh project in neighbouring Belgium.
TenneT said the BESS could also provide additional flexibility using bilateral contracts with network operators or through market-based congestion management, although the TSO warned it was important that batteries do not worsen grid congestion.
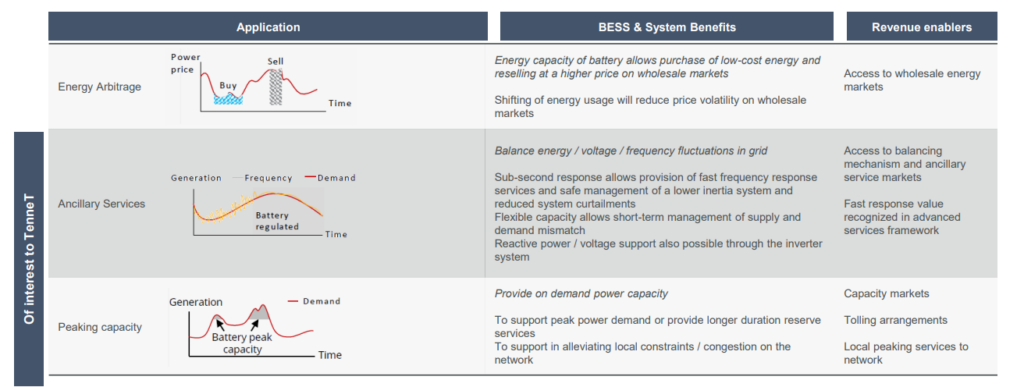
It illustrated how the BESS could be used, what the system benefits are, and how the BESS could be monetised in the table below.
Alongside large-scale BESS, TenneT has also modelled the quantity of other BESS applications which could help the grid. By 2030, it forecast 2.2GW of EV batteries (presumably V2G or V2L-enabled), 4.2GW of ‘household batteries’ and 3.7GW of ‘solar PV batteries’ in order to help with grid flexibility, alongside the 9GW of grid-scale systems.
It also provided a snapshot of what the geographical spread of the batteries would need to look like.