Chicago, Illinois-headquartered independent power producer (IPP) Hecate Energy has advanced one of its standalone battery storage facilities, located in the City of Haverhill in Essex County, Massachusetts, US.
The developer recently filed permitting documents for its Ward Hill BESS facility with the Haverhill Conservation Commission and presented plans for the project with ISO New England’s Reliability Committee last month.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
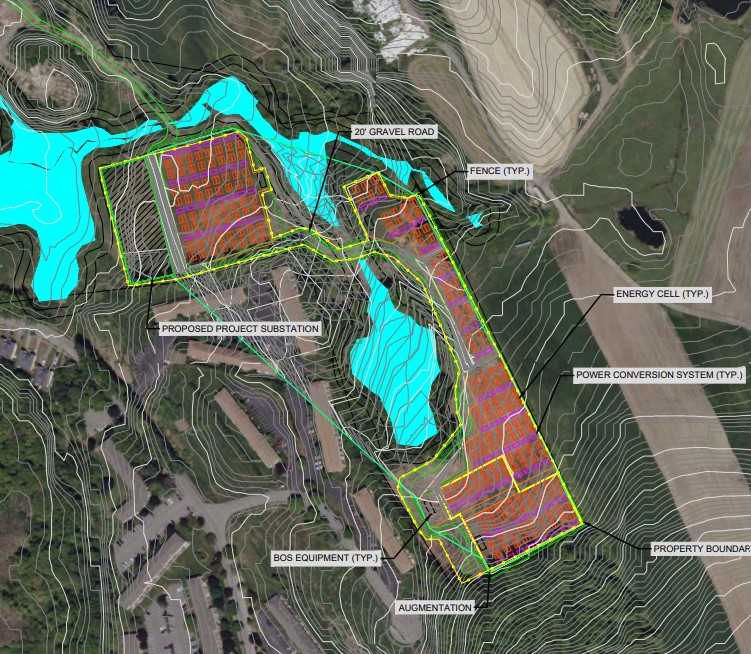
310MW/1,240MWh BESS project using CATL technology
In accordance with the Massachusetts Wetlands Protection Act, last month, Hecate Energy filed an Abbreviated Notice of Resource Area Delineation (ANRAD) application with Haverhill’s Conservation Committee seeking clarification on the wetland resource area boundaries for the proposed project.
The application revealed that Hecate Energy’s Ward Hill BESS project – located at 1160 Boston Road, Haverhill, Essex County, Massachusetts – will have a capacity of 310MW/1,240MWh and utilise CATL’s EnerX storage containers.
The EnerX BESS solution is one of several battery units produced by CATL offering 5.64MWh of capacity over a four-hour duration. Also included in CATL’s range is the Tener BESS unit, which the battery manufacturer claims has zero degradation over the first five years of operation.
ISO New England grid connection
Hecate Energy also recently presented plans for the Ward Hill project to ISO New England’s Reliability Committee – a technical advisory group overseeing system design and reliability standards for the New England grid.
During the recent August meeting, potential impacts of Hecate Energy’s Ward Hill BESS project were discussed with the Vice President of Transmission & Interconnection at Hecate Energy, Aruna Ranaweera. The project is expected to connect to the ISO New England grid via National Grid’s Ward Hill 345kV substation (queue no. 1252).
After carrying out further analysis, the reliability committee will make a recommendation to ISO New England stating how much of an impact the proposed project will have on the surrounding local grid.
Hecate Energy first filed an ISO New England interconnection request for the Ward Hill project in April 2022, which is scheduled to come online by 1 June 2026.
Repsol acquisition and lawsuit
In June 2021, Repsol acquired 40% of Hecate Energy, marking the Spanish multinational energy company’s first move into the North American renewable energy sector.
Under the terms of the original deal, the founders of Hecate Energy had a right to sell the remaining 60% of the company to Repsol through a put option. According to Repsol’s recent financial report released in July 2024, both parties were discussing this next acquisition, but were also considering “possible transaction alternatives”.
However, this month, the founders of Hecate Energy filed a lawsuit against Repsol for breaching the agreement to acquire the remaining shares – accusing Repsol of delaying and obstructing the acquisition process beyond the contracted deadline of 10 July 2024.
Standalone energy storage portfolio
Hecate Energy claims to have a 40GW development portfolio and states, and developed over 47 solar and storage projects exceeding 11.1GW, that are now operational.
The company also claims to have a pipeline of 6GW+ in standalone storage assets through a joint venture with infrastructure investment firm InfraRed Capital Partners, known as Hecate Grid, which launched in 2018.
As reported by Energy.Storage-news, the joint venture recently secured a US$125 million letter of credit facility with Japanese multinational bank Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group (MUFG).






