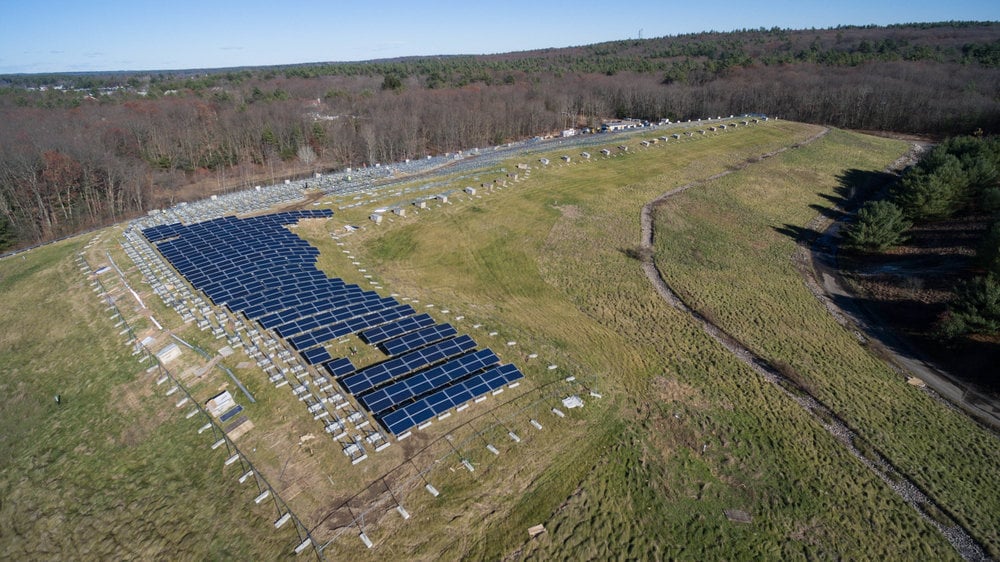
ISO New England, operating the high-voltage grid and wholesale electricity markets in the northeastern US region, has requested separate classification of energy storage as a transmission asset.
While electricity storage systems can be used for a wide variety of applications on the grid, their deployment as an enhancement to the operation of the transmission grid is not yet valued in most parts of the world.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
In a filing made just before the end of last year with US federal energy regulator FERC, ISO New England (ISO-NE) has bid to change that in its service area, notifying FERC that revisions to its Tariff and Transmission Operating Agreement (TOA) allow storage facilities to be planned as so-called ‘Storage as Transmission-Only Assets’ (SATOAs).
The regional transmission operator (RTO) made its filing together with representation of stakeholders in the New England Power Pool (NEPOOL) and New England Participating Transmission Owners (PTOs).
NEPOOL’s membership comprises generation, electricity supply, transmission companies, publicly owned entities, trade groups and various other categories of ISO New England stakeholders.
The filing requested that FERC accept the revisions “without modifications or conditions,” but also asked that a symbolic date in the year 9998 be set as its implementation timeline, giving ISO staff time enough to develop, test and implement software system modifications that will be required.
Nonetheless, it asked for the commission to accept the revisions by 29 March 2023 at the latest, which would start the process off, at which time a deadline at the beginning of July 2024 could be set for the above modifications to be in place.
Electricity storage resources, such as large-scale lithium-ion battery energy storage systems (BESS), have historically been treated under ISO New England rules as market resources. However, with the potential effectiveness of storage as an asset class to address transmission issues more cost-effectively and efficiently, out-of-market rules tailored to accommodate it is needed, the ISO said.
Regulation should be ‘on par with traditional wires-based solutions’
The proposed rules are fairly complex, but in testimony provided in the filing, ISO New England director of transmission planning Brent Oberlin explained its key principles and framework.
Oberlin noted a couple of precedents, such as a FERC ruling in 2010 that a California pumped hydro energy storage (PHES) plant be treated as transmission on the California Independent System Operator (CAISO) grid.
Storage as a transmission asset should be subject to regulatory treatment “on par with traditional wires-based regulated transmission solutions,” Oberlin said. SATOA facilities could be any relevant technology, which could include batteries, compressed air, hydroelectric storage and others, connected to the transmission grid at 115kV or higher voltage.
One important stipulation is that SATOA assets should connect directly to ISO-NE pool transmission facilities (PTFs), charging and discharging to and from the PTF alone.
ISO-NE is responsible for planning the region’s electricity system over a multi-year timeline, and Oberlin discussed how SATOAs will be incorporated into planning, and said the revision proposes limiting the aggregate amount of SATOAs in the area to 300MW charging and 300MW discharging capability, and no more than 30MW per individual facility.
Limits would be imposed to prevent overburdening grid operators and reduce risks from system misuse or failures, while the systems would charge only from the high-voltage grid to prevent putting equipment such as generation and inverters between the grid and storage system’s operation.
A recent study produced not too far away in New York argued a similar case for energy storage as transmission. Written by consultancy Quanta Technology and commissioned by trade and technology group NY-BEST, the paper found that the many benefits of storage as a transmission asset (SATA) as it was called in slightly different terminology, included the ability to reduce renewable energy curtailment and alleviate grid congestion.
Only a small handful of actual storage as transmission projects, or, to use yet another term, storage as a non-wires alternative (NWA) to investment in transmission infrastructure, have actually gone ahead or been contracted around the world.
One major example is Germany’s ‘Grid Booster’ projects that transmission system operators (TSOs) have been given approval for, with one 250MW BESS contract awarded to storage technology provider Fluence.
Energy-Storage.news’ publisher Solar Media will host the 5th Energy Storage Summit USA, 28-29 March 2023 in Austin, Texas. Featuring a packed programme of panels, presentations and fireside chats from industry leaders focusing on accelerating the market for energy storage across the country. For more information, go to the website.