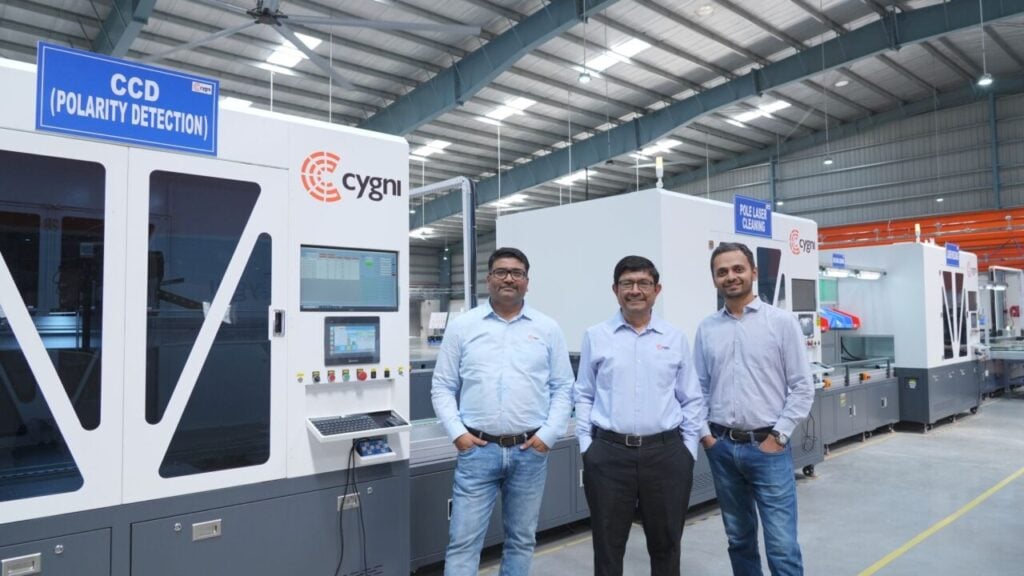
Cygni Energy, a manufacturer of electric vehicle battery packs and battery storage systems, has opened a ‘gigafactory’ in India.
The first phase of an assembly plant with 4.8GWh annual production output in Hyderabad, Telangana, was inaugurated at an event yesterday (30 April).
The ceremonial opening was attended by dignitaries including the Telangana state special chief secretary for IT, industries & commerce and sports, Jayesh Ranjan.
The company announced the opening via social media site X.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
“We’re thrilled to share a milestone moment for Cygni Energy—today we inaugurated of our state-of-the-art BESS Gigafactory at Maheshwaram, Hyderabad!” the company tweeted.
Cygni Energy manufactures battery packs for electric two-wheeler and three-wheeler vehicles and stationary battery energy storage systems (BESS), largely for the commercial and industrial (C&I) market segment.
Speaking at the ceremony, a company representative said the site was selected around two and a half years ago after an extensive search.
Cygni, headquartered in Hyderabad, incubated its technologies at IIT Madras Research Park in Chennai, although Telangana government official Ranjan claimed via X that the factory had been located in his state “because of our superior infra and policies.”
According to coverage by newspaper The New Indian Express, Cygni Energy said around IR1 billion (US$11.8 million) has been invested in the facility which occupies a 5-acre site in Hyderabad’s Electronics Manufacturing Clusters (EMC).
The company plans to more than double the production capacity with Phase II to 10.8GWh, The New Indian Express quoted Venkat Rajaraman, Cygni Energy’s CEO and founder, as saying.
The Cygni factory opening is the latest in a number of BESS assembly plant announcements from India.
In late 2023, what is thought to have been the first units made at a factory in India rolled off the production line from Tata AutoComp Gotion Green Energy Solutions. The company is a joint venture (JV) between an automotive and power solutions subsidiary of India’s Tata Group and Chinese battery manufacturer Gotion High-Tech.
The first BESS units off that production line, in Pune, Maharashtra, were supplied to a 120MW stationary storage project by Tata Power. The JV’s factory has a planned total production output of 6GWh annually once fully ramped.
Last year Good Enough Energy announced at an industry event that it would build a factory in the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir, with an initial 7GWh production capacity, ramping to 20GWh.
However, while system and equipment assembly plants are starting to go into production at scale in India, battery cell manufacturing is still at a much earlier stage. The Union government is seeking to support cell manufacturing through its Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme. In 2022, it selected an initial 50GWh of so-called advanced battery cell annual manufacturing capacity plans to benefit from the PLI scheme.