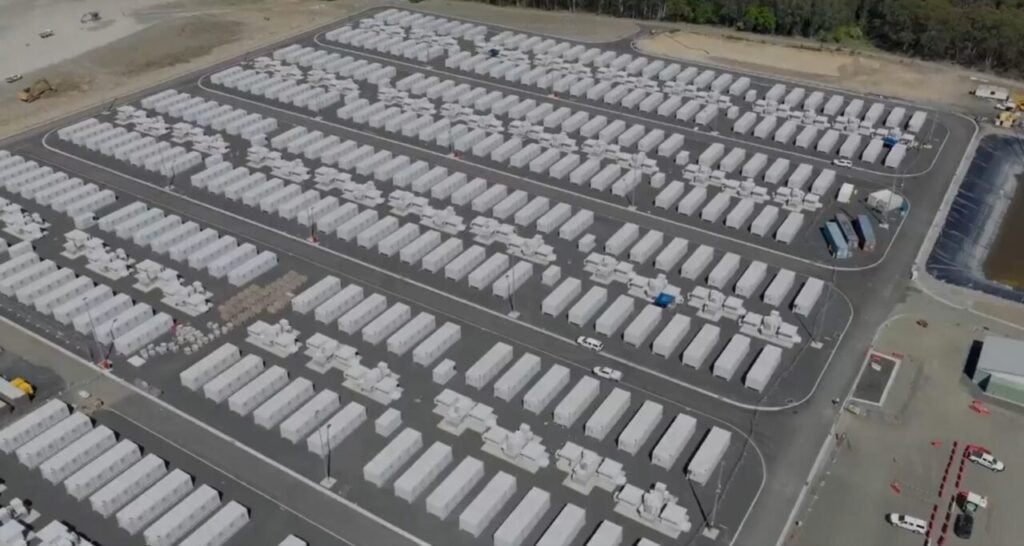
Utility Origin Energy has announced the commercial commencement of Eraring Battery 1, a 460MW/1,770MWh battery energy storage system (BESS) located in New South Wales, Australia.
Greg Jarvis, executive general manager, energy supply and operations at Origin Energy, took to LinkedIn today (7 January) to unveil the milestone, stating that the project represents the “largest approved BESS in the Southern Hemisphere”.
The battery storage system is designed to store daytime solar electricity for release during peak demand periods, providing critical grid services to support Australia’s renewable energy transition.
Commercial commencement of Eraring Battery 1 signifies that the BESS site is currently connected to and operating within the National Electricity Market (NEM), which spans Australia’s eastern states and territories.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
The Eraring Battery 1 project was developed through partnerships with multiple contractors, including Wärtsilä, Enerven, Jacobs, Lumea and Transgrid. Origin Energy first energised the initial stage of the Eraring battery storage project in 2024 as part of a broader development programme.
Wärtsilä served as the primary technology provider for the battery storage system, continuing its established relationship with Origin Energy. Wärtsilä confirmed recently that it has been selected for the next Eraring expansion project.
Origin Energy received approval in July 2024 to construct the 240MW/1,030MWh second stage, which is being equipped with grid-forming advanced inverters to aid network stability. Wärtsilä has been hired for all announced stages, which will increase the total capacity of the Eraring site to 3,160MWh.
The 460MW power output enables the system to provide substantial grid services, including frequency regulation, voltage support and energy arbitrage services.
Meanwhile, the 1,770MWh energy capacity allows for approximately 3.8 hours of continuous discharge at full power output, positioning the system to address peak demand periods and provide renewable energy firming services.
This capacity puts it ahead of Akaysha Energy’s 1,680MWh Waratah Super Battery. However, in terms of power output, the Waratah BESS still holds the top spot with 850MW. In October last year, the Waratah Super Battery experienced a catastrophic transformer failure as it continued to work towards full operational status.
In November 2025, Origin Energy was granted AEMO approval of NEM connection agreements for a 300MW/650MWh grid-forming BESS project at Mortlake Power Station in Victoria.
Several other gigawatt-hour-scale battery storage projects are at various stages of development across Australia. For instance, Quinbrook Infrastructure Partners’ proposed Gladstone State Development Area (GDSA) Energy Hub Project in Queensland would feature a 780MW/6,240MWh (8-hour duration) BESS in combination with gas turbines.
The Energy Storage Summit Australia 2026 will be returning to Sydney on 18-19 March 2026. To secure your tickets and learn more about the event, please visit the official website.