
Renewable energy developer ACE Power has submitted a 2,000MWh battery energy storage system (BESS) in Queensland to Australia’s Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation (EPBC) Act.
The developer, which recently secured federal government approval for 5.6GWh of BESS in the EPBC Act, intends to develop the Burdekin BESS near Clare, around 76km south of Townsville, a coastal city in northeastern Queensland.
The 500MW/2,000MWh grid-connected BESS will operate within the National Electricity Market (NEM), which covers Australia’s eastern coast and Tasmania.
According to the EPBC Act application, the developer is being pursued via ACE Power’s subsidiary, Burdekin Solar Farm. Development of the site started in 2015, and the initial focus was to build a solar PV power plant with the option of a co-located BESS.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
Instead, the project proposer has now submitted a change to the application to the Burdekin Shire Council to reflect that the site is now a standalone BESS, and that the solar component of the project will be separate and optional in the future.
The BESS will connect to the existing network via a new Powerlink substation, Millaroo. A 275kv single-tower double-circuit overhead transmission line will link the Millaroo substation to the existing Haughton River-Strathmore 275kV Powerlink overhead transmission line. You can find the site layout below.
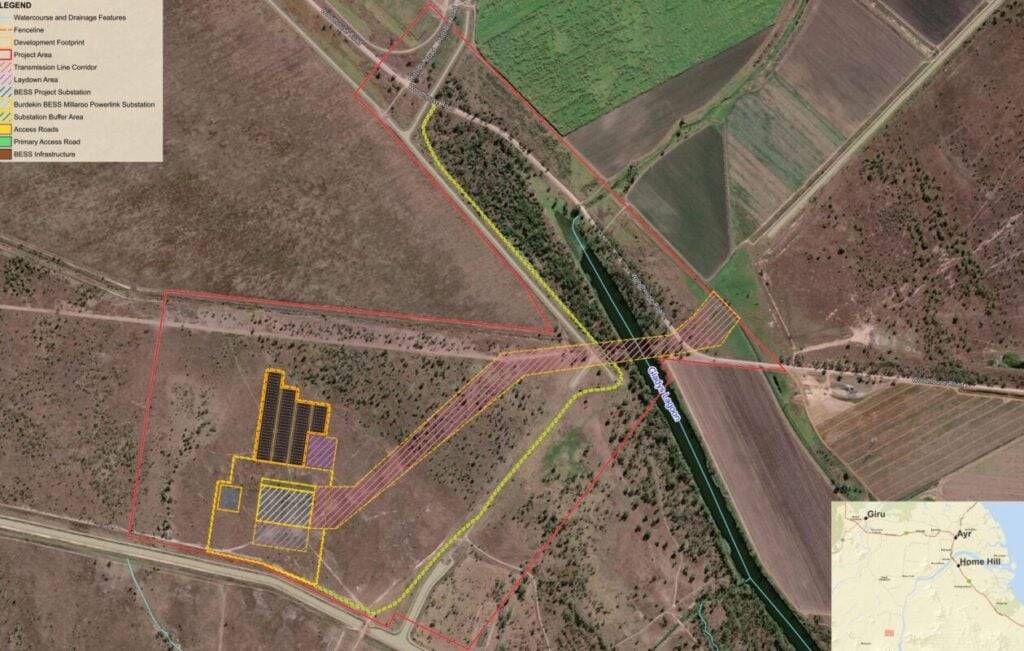
The site’s construction phase is anticipated to take 18 to 24 months. The BESS will have an operational lifespan of 35 years and will assist with grid reliability, network frequency, and voltage stabilisation. It will also store renewable energy for discharge during periods of peak demand.
Once the operational lifespan has been reached, the developer will decide whether to decommission the site or replace the plant and extend its life for an additional 25 to 30 years. The application said this will be subject to market and economic factors at that time.
Readers of Energy-Storage.news will likely be aware that ACE Power’s Burdekin BESS will be in close proximity to the cancelled 5GW/120GWh Pioneer-Burdekin Pumped Hydro Project, which was once touted as the world’s largest pumped hydro site.
ACE Power’s Australian energy storage portfolio
ACE Power is developing several renewable energy projects in New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria, South Australia, and Western Australia, including BESS.
Perhaps the most notable of its projects is the Hillview Energy Hub Project, which is set to feature around 300MW of solar PV and 300MW wind generation in New South Wales. The project will also feature the company’s largest BESS in its portfolio, a 1,000MW/4,000MWh 4-hour duration system. This is dependent on site constraints and market conditions.
It is also worth noting that the project will be situated in the New England renewable energy zone (REZ), aiming to deliver up to 8GW of new transmission capacity to help deliver further renewable energy generation to the grid.
Earlier this year, the developer submitted plans for a 3.6GWh 4-hour duration BESS in Queensland to the EPBC Act. Called the Nebo BESS, the 900MW project, which will cover 97 hectares, will also include an extension to Powerlink’s Nebo substation. Two underground 275kV circuits will connect the project to this substation.
The project will be located near the rural town of Nebo in the Isaac region, around 956km north of the state capital, Brisbane. It will import electricity from the grid, which will then be stored and exported during peak demand.
According to documents submitted to the EPBC Act, the project will have two 450MW stages that could be developed separately or concurrently. Although the specific details of the BESS technology were not disclosed, the company confirmed that it will utilise lithium-ion technology.





