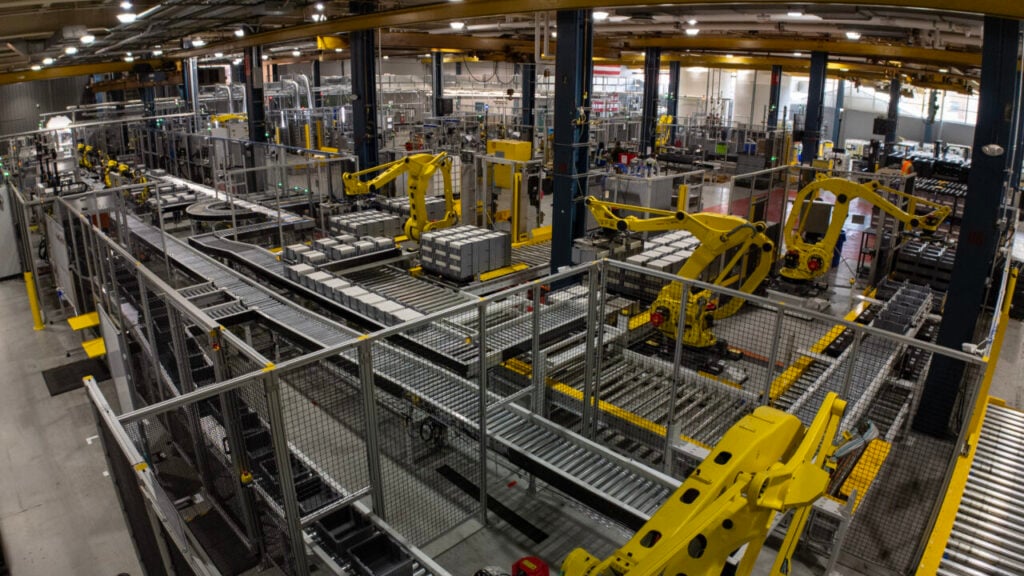
Zinc hybrid cathode battery and storage system maker Eos Energy Enterprises expects 2025 revenues to be roughly ten times higher than last year’s.
The startup, headquartered in New Jersey, US, reported its fourth quarter and full-year 2024 financial results this week (4 March). During the twelve months, the company earned US$15.6 million, in line with revised revenue guidance issued earlier in the year.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
For 2025, Eos has issued guidance for revenue between US$150 million and US$190 million. This massive jump will be down to the manufacturer’s ability to increase production volume at its first semi-automated production line, part of a plan to establish 2GWh of annual production capacity at its Turtle Creek, Pennsylvania, factory.
The company makes a zinc-based battery that it hopes to position as an alternative to lithium-ion (Li-ion) for medium to long-duration energy storage (LDES) applications requiring 6-hour to 12-hour discharge at full-rated power.
It went public via a special purpose acquisition company (SPAC) merger in 2020, listing its shares on the Nasdaq exchange, around the time several other firms in the energy storage space also went public through business combinations with ‘blank cheque’ SPACs.
While the average share price hit a high of US$28.83 in January 2021, their value subsequently plummeted. Several times last year, it fell below US$1.00 but has recovered somewhat and was at US$4.53 as markets closed yesterday.
Eos reported a gross loss of US$83.3 million for the year, a US$685.9 million net loss attributable to shareholders and an adjusted EBITDA loss of US$156.6 million.
However, CEO Joe Mastrangelo highlighted his team’s delivery of “significant results” during 2024 and said Eos is “hyper-scaling its capacity expansion to secure larger orders and deliver for customers and shareholders.”
Eos positioning as ‘Made in America’ brand
Along with the first of its new production lines going into action, Eos secured significant cost reductions in the Z3 battery module, which powers its Znyth brand DC BESS solution, Mastrangelo said.
In addition, the company now claims that its pipeline of customer opportunities that it hopes to convert into orders stands at more than US$14 billion, equivalent to around 55GWh of systems. Its customer order backlog stood at US$682 million at the end of the year, representing around 2.6GWh. That was a 28% increase from the end of 2023.
It also secured financing from an affiliate of alternative investment advisor Cerberus Capital Management and closed a loan guarantee with the US Department of Energy (DOE) Loan Programs Office (LPO) in December.
Eos may have been one of the last clean energy startups to get LPO funding in the final days of the Biden-Harris administration (Premium access), closing an agreement for US$303.5 million, of which a first US$68.3 million has been secured.
As has been widely reported, the LPO has been inactive since Donald Trump took office and office head Jigar Shah resigned in January, although its website is still live at the time of reporting. While it appears any loans still in negotiation have been comprehensively cancelled, some media outlets and commentators have speculated the Republican administration may also seek to cancel loans already closed.
Eos will be hoping that its position as a ‘Made in America’ brand offering skilled jobs and manufacturing within the US and outside of the lithium-ion supply chain, which is heavily dependent on imports, will continue to make it attractive to its government.
Likewise, the company would benefit from domestic content bonuses on tax credits introduced under Biden. It noted in its Form 10-K filing of results with the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) that it would be at economic risk in the event of Congress repealing upstream production tax credits (PTCs) and downstream investment tax credits (ITCs).
Eos is now seeking a new factory site to expand into and has narrowed its search to eight US states that have been issued requests for proposals (RfPs). With the addition of three more production lines, it hopes to add another 6GWh of annual production capacity to the 2GWh it is developing in Pennsylvania.
US$8 million Naval Base of San Diego order secured
On the same day its results were announced, the company said it had secured an order worth US$8 million to deploy a zinc-based BESS solution at a US Navy base in San Diego, California.
Fully funded by the California Energy Commission (CEC), the project will supply resilient power to the US Navy’s western fleet, including critical must-run functions and comes after the US Department of Defense (DOD) prohibited the use of battery equipment from several prominent Chinese manufacturers at its facilities.
The DOD designated companies, including CATL, as ‘Chinese Military Companies’ in a list published in January, even before Trump took office, a designation that CATL described as a “mistake,” arguing that it “has never engaged in any military-related business or activities.”
In its Form 10-K, Eos outlined the scale of the challenge it faces to displace lithium-ion even in longer-duration market segments, noting that customers seeking higher power density would likely opt for the incumbent technology and that breakthrough cost reduction for Li-ion would also be a competitive threat even for long-duration applications.
That said, the manufacturer claimed to have achieved a 77% volume-adjusted cost reduction in Z3’s production since its launch and pointed to partnerships with insurance company Ariel Green and software-focused BESS system integrator FlexGen among recent developments that Eos said validated its approach and technologies.
Read more Energy-Storage.news coverage of Eos Energy Enterprises.