
Itochu, a major Japanese corporation which has sold over 330MWh of residential battery storage systems in its home market, has invested ¥1 billion (US$9.35 million) in TRENDE, a renewable energy retailer which counts utility company Tokyo Electric Power among its major shareholders, with a view to launching a range of renewable energy and storage-enabled services.
TRENDE was started up by Tokyo Electric, one of the 10 regional monopoly utility companies across Japan which are also responsible for the transmission and distribution network in their service areas. Japan’s electricity market is undergoing a gradual deregulation and unbundling process and hundreds of new electricity businesses have been set up in anticipation of increased customer fluidity.
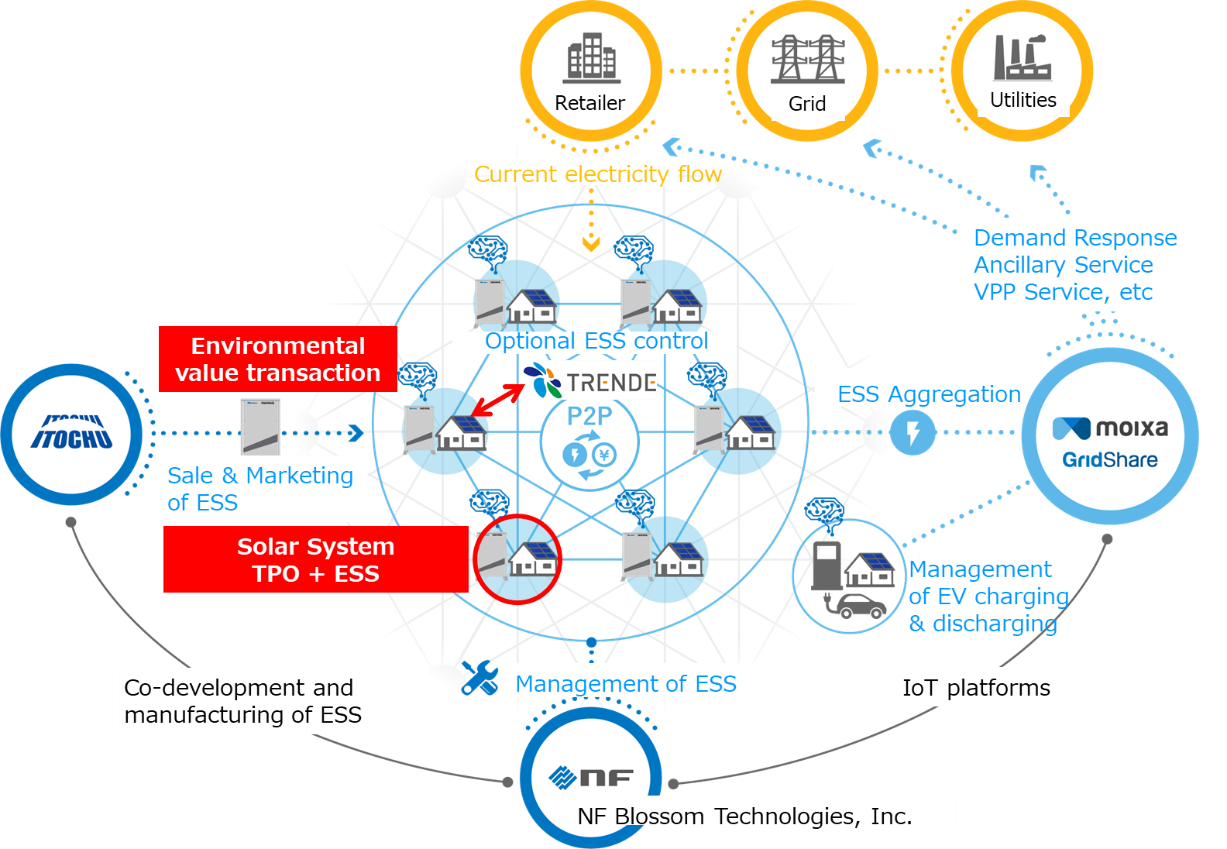
With other investors onboard including Japanese petroleum company Idemitsu and the Dubai Electricity and Water Authority as well as Itochu, TRENDE has launched both a simplified utility retail plan business and a no-money-down, third-party leasing prosumer solar energy installation business.
Itochu meanwhile is involved in everything from homebuilding to metals and minerals. It is involved in the lithium battery value chain from the upstream of lithium extraction, handling certain materials essential for the creation of batteries from raw materials like spodumene and fluorite to intermediate materials such as lithium hydroxide and lithium carbonate, battery materials such as cathodes, binders and separators.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
It doesn’t make the batteries themselves, it buys them back in from partners like LG Chem and Samsung SDI, but then assembles complete systems using those batteries and sells them to customers packaged in various formats for residential and small commercial use in Japan and elsewhere. The battery systems are controlled and optimised using Gridshare, an artificial intelligence (AI) software platform developed by UK energy storage company Moixa – in which Tokyo Electric was actually an investor before the Itochu partnership, bringing the start-up to Itochu’s attention.
Pair combining to build on success of selling systems for backup
Itochu said it has sold 33,000 units – or 100MW / 330MWh – of one of its range of ESS, Smart Star, which is a 3kW / 9.8kWh model aimed at enabling full backup of a household load, in Japan. While the economics of selling battery storage are not yet considered compelling in their own right, the demand for backup power in the event of natural disasters such as earthquakes and typhoons in Japan is driving demand. The expiration of 10-year feed-in tariffs (FiT) which began in 2019 is also providing an impetus for retrofitting batteries to solar systems in Japan.
TRENDE said yesterday that it has successfully completed a Series B funding round from Itochu, for ¥1 billion of combined equity and unsecured convertible bonds. The pair had already launched a tariff based on trading energy from residential storage but are expected to expand the scope of the partnership further to include no-money-down business models and leverage their technologies and customer base to increase japan’s share of renewable energy.
“We’re extremely pleased to have ITOCHU as an investor and partner in our mission to accelerate the widespread adoption of renewable energy in Japan. Bringing together TRENDE’s expertise in distributed energy with Itochu’s leadership in energy storage systems creates a really powerful combination,” TRENDE CEO Tadatoshi Senoo said.
“We are jointly developing a new service that combines distributed solar generation with energy storage and expect to release it later this year.”
Itochu said that in future the pair also want to start up new business models using renewables and batteries including peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading. Last year, TRENDE set up a P2P trading trial using blockchain to enable the bi-directional flow of power. At present however, Japanese grid regulations do not allow for electricity storage systems to feed power back into the grid, or for customers to sell electricity to utilities, which is a barrier to the development of virtual power plants (VPPs) and other advanced technology-based applications.





