South Korea’s KEPCO trials vanadium flow batteries at R&D centre
South Korea’s largest electric utility will try out seven vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB) energy storage systems made by Invinity Energy Systems.
The 1.5MWh deal was announced yesterday by Anglo-American flow battery company Invinity, which said Korea’s Hyosung Heavy Industries, part of the Hyosung Group conglomerate, has put in the order.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Electrical equipment manufacturer Hyosung’s energy storage division has been contracted for or delivered battery projects in various territories, including South Africa and the UK, and will be putting the flow battery systems at a Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO) R&D center.
The deal follows the signing in April of a memorandum of understanding (MoU) between Invinity and Hyosung Heavy Industries to collaborate on commercialising the flow battery technology in South Korea and international markets.
The VRFBs will be installed at the KEPCO facility in Naju City, where the utility will gather performance data. Depending on how that goes, KEPCO could qualify the devices for wider use and Invinity said it could lead to grid-scale project opportunities with both KEPCO and Hyosung.
Initial payments will be made this year and commissioning should be completed by mid-way through 2023, according to Invinity.
Battery storage developer launches automated bidding tool
US grid-scale battery storage developer Key Capture Energy has become the latest player in the market to launch its own energy bidding software tool for wholesale market trades.
Like Tesla’s Autobidder or Wartsila’s Intellibidder, the product, called MarketCapture, the tool uses artificial intelligence (AI) and market and system data to make smart decisions on which energy trades to make and places bids.
Now fully operational and being deployed by the company for its own and third-party projects in Texas’ booming ERCOT market, Key Capture Energy plans to have it in use in the New York Independent System Operator (NYISO) market early next year and then roll it out further across the US.
MarketCapture is suitable for day ahead bidding applications and comes with real-time bidding and optimisation capabilities at 5-minute intervals. Real-time bidding and optimisation are powered by the WattBot web-based electricity monitoring platform.
Key Capture Energy claimed it is fully automated to provide reporting on a daily, weekly and monthly basis, which can be measured against a “100% perfect forecast knowledge metric,” and is updated with accurate market intelligence including price trends and asset performance.
“By showcasing how this AI-driven optimisation tool performs in the high stakes and challenging ERCOT market, Key Capture Energy is setting a bold standard for energy storage asset optimization forecasting and demonstrating the full potential for renewable energy projects in ensuring a reliable and resilient energy grid,” Key Capture Energy CEO Jeff Bishop said.
Bishop has been vocal in past interviews with Energy-Storage.news on the growing importance of smart software for battery storage and in particular the need to have in-house software and digital expertise. Yesterday the company said the development of MarketCapture and its integration with WattBot comes after two years of focus by its software teams.
Key Capture Energy, which tends to conduct an owner-operator business model, has 380MW of Texas projects in operation.
Maryland utility completes first BESS under state pilot programme
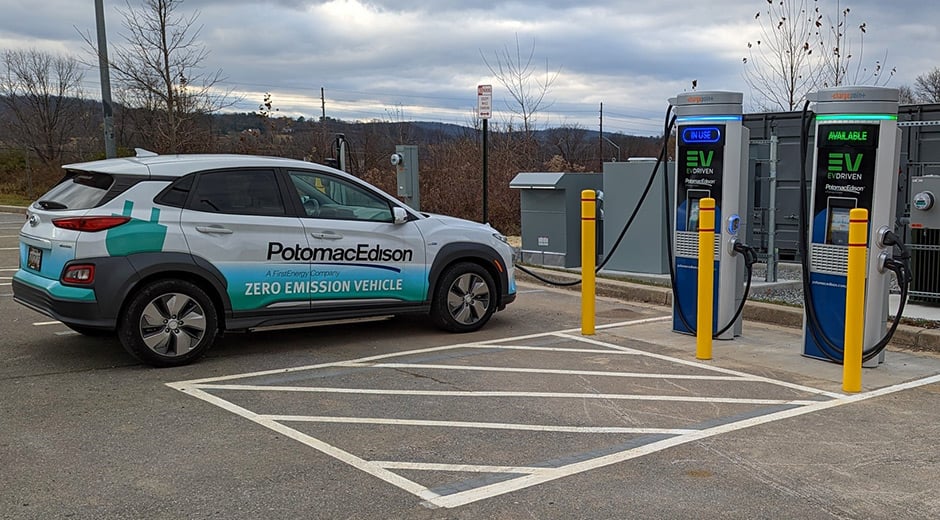
US utility company Potomac Edison has completed its first battery energy storage system (BESS) project in Maryland, under a state energy storage pilot programme.
Potomac Edison will own and operate the 500kW BESS, which is integrated with electric vehicle (EV) charging facilities in Maryland’s Frederick County.
Announcing its completion yesterday, the utility will study how the system can enable the site’s two DC fast-charge units and a Level 2 charging station to reliably deliver power to EVs without straining the grid. It will lower the chargers’ grid use at peak times and ensure their uninterrupted use.
It will soon be joined by another BESS project Potomac Edison, a subsidiary of listed electric utility holding company FirstEnergy Corp, proposed to Maryland regulators through the Energy Storage Pilot Program established after Governor Lawrence Hogan signed it into law in 2019.
Each of the state’s investor-owned utilities (IOU) was ordered to solicit offers to build energy storage projects and then put them up for approval by the regulatory Maryland Public Service Commission. Potomac Edison’s two projects were given approval in May 2021, as reported by Energy-Storage.news.
As noted in a 2020 interview with then-CEO of the national Energy Storage Association Kelly Speakes-Backman, herself a Maryland native and a former state commissioner, the programme is notable for not only assessing the technology involved in storing energy, but also in exploring different applications and ownership models.
Potomac Edison’s next BESS project is a 1.75MW system in Allegany County, which will provide backup power to a small town and expected to be in service in 2024. The utility has about 420,000 customers, mostly in Maryland with a few in parts of West Virginia.