
Plus Power has closed financing for a 150MW/300MWh standalone battery energy storage system (BESS) project in Massachusetts, US.
The developer said yesterday (13 June) that it has raised construction and term financing for its Cranberry Point BESS asset in the Massachusetts town of Carver. It claims that it will be the first large-scale standalone battery storage facility to connect to the ISO New England grid.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
Financing was raised through First Citizens Bank and Nord LB, which acted as coordinating lead arrangers, along with joint lead arrangers Investec and Siemens Financial Services. Investec is the administrative agent, and US Bank serves as the depositary bank.
Plus Power is targeting completion of the project in Q2 2025. Along with Cross Town Energy Storage, a 175MW/350MWh project that the company is developing in Maine, Cranberry Point was a winner in an ISO New England Forward Capacity Auction (FCA) with long-term contracts awarded at a preliminary price of US$3.58 per kilowatt-month, as announced in February.
The Plus Power projects were among 1,800MW of winning energy storage projects including more than 700MW of new build, demonstrating a rapid growth in secured storage capacity at auctions, from just 5MW cleared in a 2018 FCA when batteries first became eligible.
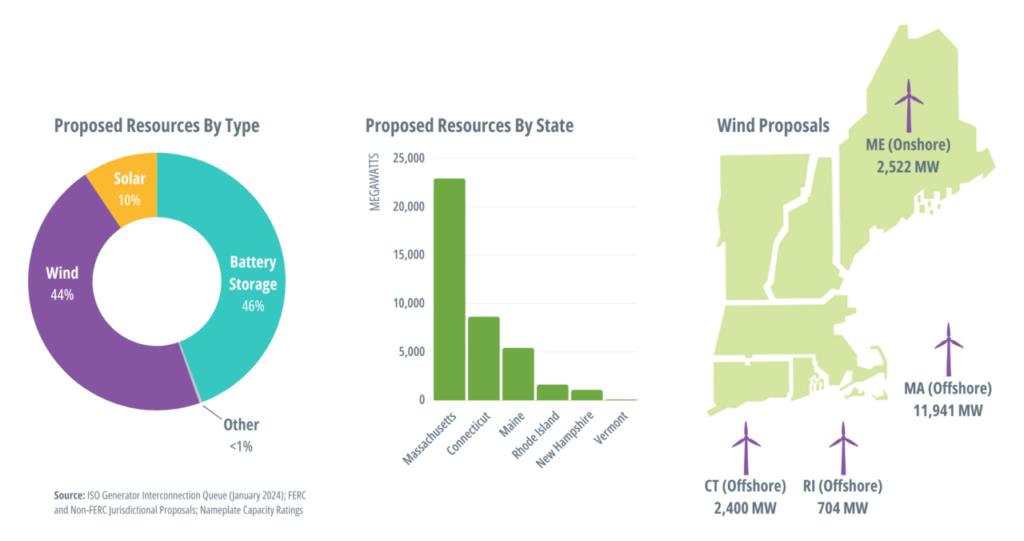
BESS represents 46% of projects in ISO interconnection queue
According to ISO New England, the independent system operator (ISO) that oversees the electric system and wholesale power market in the five New England states, there was only 90MW of battery storage available to it for dispatch as of the beginning of this year according to ISO data on its resource mix.
These are thought to comprise mostly distributed scale and small front-of-the-meter (FTM) solar-plus-storage projects, incentivised over the past few years in particular by the Massachusetts Clean Peak Standard for grid emissions and Solar Massachusetts Renewable Target (SMART) incentive scheme.
In addition, the ISO can currently call on 1,800MW of pumped hydro energy storage (PHES) from two existing plants.
However, as of January 2024, 46% of proposed projects totalling 40,000MW in the ISO New England Interconnection Request Queue were battery storage, the biggest share by technology, with wind second (44%), solar representing 10% and the remaining 1% from other technologies.
For the title of first, Plus Power appears to have overtaken rival developer Eolian, which had the biggest project to win in the FCA auction with its 250MW/500MWh Medway Grid BESS.
Both Cranberry Point and Medway Grid became embroiled in a dispute that one local news outlet had described as a regulatory “black hole”. Planners in the towns of Carver and Medway enacted moratoriums on BESS development in 2022 and 2021, respectively, arguing that local zoning laws did not fully encompass the relatively new technology.
That state of regulatory limbo ended in late June 2023, as the Massachusetts Department of Public Utilities (DPU) granted local Zoning Law exemptions, effectively clearing the path for the projects to go ahead.
Energy-Storage.news has contacted Eolian for a status update on the Medway Grid project and will update this story accordingly when a response is received.
Plus Power said that its Cross Town Energy Storage project began construction in April 2024, while Cranberry Point began construction in December 2023. Both facilities’ FCA contracts will be for delivery from 2025 through 2031. The developer noted that Cranberry Point comprises a significant portion of Massachusetts’ 1,000MWh by 31 December 2025 energy storage policy target, which it will count towards.
According to Plus Power, Cranberry Point is also the first battery project in the Commonwealth state to reach financial close that will benefit from the Massachusetts Clean Peak Energy Certificates (CPECs) scheme, which is an expansion of the Clean Peak Standard to enable batteries to be compensated for their role in shifting energy use from more polluting peak times to off-peak periods.
Other recent Plus Power projects reported by Energy-Storage.news include the 90MW/360MWh Superstition BESS in Arizona for which the developer secured US$82 million tax equity financing from Morgan Stanley a couple of months ago, and Hawaii’s biggest standalone BESS project to date, the 185MW/565MWh Kapolei Energy Storage (KES) project which is equipped with grid-forming inverters to provide inertia and other system support services to utility Hawaiian Electric Co (HECO). Kapolei went online at the beginning of this year.
In October 2023, Plus Power concluded US$1.8 billion financing for five projects in Arizona and Texas, including what is thought to be the largest financing for a single project to date, US$707 million raised for the 250MW/1,000MWh Sierra Estrella BESS project in Arizona.
This article has been amended to reflect that the FCA contracts for Cranberry Point and Cross Town are from delivery from 2025-2031, not 2027-2031 as was originally stated. Also, of the two projects, only Cranberry Point will contribute towards the Massachusetts energy storage target, as Cross Town is sited in Maine.






