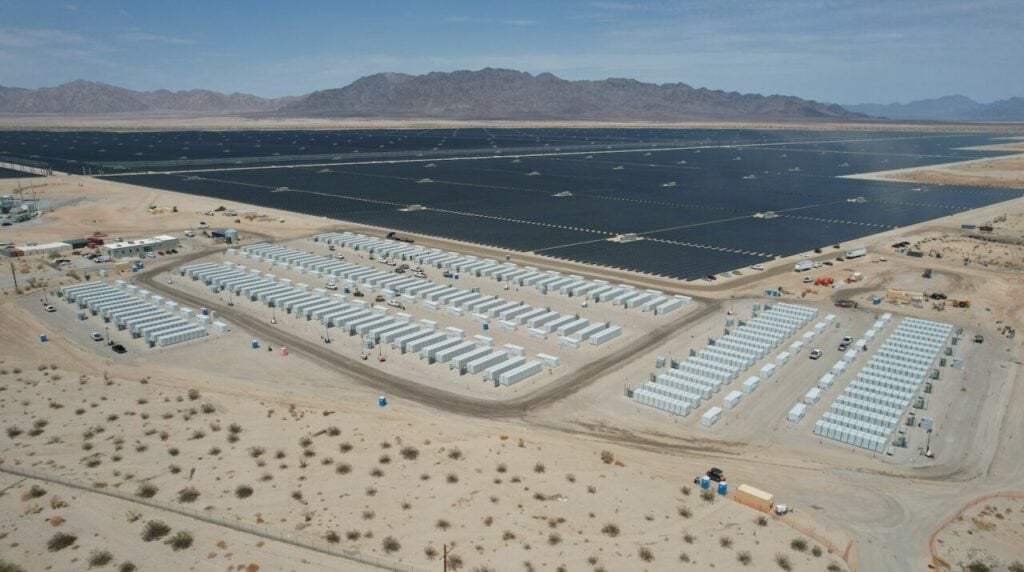
Independent power producer (IPP) NextEra Energy Resources (NEER) is set to build a 600MW standalone BESS facility in the City of Ontario, California, half of which is tied to a utility agreement.
A website dedicated to the Roadhouse Energy Storage project was recently launched by NEER, revealing certain details surrounding the project including the developers intentions to invest US$535 million into the standalone BESS.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
The Roadhouse project is one of NEER’s most advanced pipeline projects, having already secured an offtake agreement covering a portion of the project’s capacity with a public utility, as well as an interconnection agreement with the California Independent System Operator (CAISO).
300MW/1,200MWh worth of BESS capacity at US$18.76/kW-month fixed rate
The proposed Roadhouse Energy Storage project will utilise lithium-ion battery technology encompassing a 20-acre site located approximately 1.8 miles south of Champagne in the City of Ontario, California.
NEER has already secured a power offtake agreement for half of the project’s capacity with Anaheim Public Utilities (APU), approved by the utility’s board of directors at an April 24 2024 meeting.
Under the terms of the energy storage agreement (ESA), the Roadhouse project will supply APU with 300MW/1,200MWh worth of energy, capacity, and ancillary services for a period of 20 years at a US$18.76/kW-month fixed rate.
As stipulated by the agreement, NEER has guaranteed a battery efficiency rate of 83.1% during the first year, decreasing annually to 78.2% in the final year.
Project to provide 60% of APU’s summer peak demand
The Roadhouse project was selected by APU after the utility issued a request for proposals (RFP) in October 2023 seeking renewable energy resources in order to reach its target of having a 60% renewable portfolio by 2030.
As detailed in the agenda materials for the April APU meeting, an evaluation of NEER’s Roadhouse proposal for the RFP was carried out by software and consulting firm Ascend Analytics. As part of the suitability review, Ascend considered the project’s location, grid interconnection, dispatchability, developer experience, along with a cost-benefit assessment.
APU will be responsible for dispatching the battery, which is capable of providing 60% of the utility’s summer peak demand.
Construction on the APU portion of the project is contracted to start by April 1, 2026, with commercial operations expected by October 1, 2027.
US$7 million in annual savings put towards additional renewable resources
APU expects the ESA to cost an estimated US$71 million annually, made up of an annual US$67.5 million payment to NEER, along with a yearly US$3.5 million cost to charge the batteries. However, when considering the avoided capacity payments to CAISO, along with the project’s wholesale energy revenue, the utility expects to save an estimated US$7 million per year.
The utility has said that it will use these savings to “acquire additional renewable energy resources to meet state compliance requirements”.
CAISO interconnection agreement
The developer has secured an interconnection agreement with CAISO and utility Southern California Edison (SCE) covering 300MW for the Roadhouse project, processed as part of the system operator’s cluster 13 process (queue no. 1768).
Presumably, NEER will file a separate interconnection agreement for the remaining 300MW as part of a later CAISO cluster process. The project will connect to the CAISO grid via SCE’s Mira Loma 230kV substation.
Rapid BESS deployment in CAISO
Utility-scale BESS facilities, such as NEER’s proposed Roadhouse project, are vitally important for maintaining the California grid – a fact that was recently highlighted in a July 2024 CAISO battery storage report.
CAISO has seen a huge surge of new BESS capacity connected to its grid over the past few years, increasing from 500MW in 2020, all the way to 11.2GW as of June 2024, according to statistics from the recent report.
The report found that batteries are accounting for a significant portion of CAISO’s energy and capacity needs, especially during the early evening when net loads are at their highest. During the hours of 5pm and 9pm during 2023, batteries provided on average 5.6% of CAISO’s energy needs, which was up from 2.4% in 2022, as reported in an identical study prepared by CAISO last year.