Mitsubishi Corporation said today that it is partnering with major Japanese telecoms provider NTT to “study cooperation” in renewables, energy management using electric vehicles and battery energy storage, while according to reports, NTT is investing around US$1 billion a year in renewable energy up to 2030.
Newspaper Nikkei said yesterday that it had learned Nippon Telegraph and Telephone (NTT) will invest ¥1 trillion (US$9 billion) between now and 2030 in renewable energy generation and entering the electricity transmission and distribution (T&D) business.
Japan’s T&D network is dominated by 10 regional utility companies, but the sector has been gradually undergoing deregulation since 2016. NTT Group, which has more than 300,000 employees, could have the scale to “disrupt the dominance” of those electric companies and potentially help lower energy costs, the Nikkei report said.
NTT launched its own energy business, NTT Anode Energy, in mid-2019, with the parent company saying it would pursue business opportunities in “smart energy” and setting a target of increasing energy business sales by the Group as a whole to around ¥600 billion by the 2025 fiscal year. NTT said then that NTT Anode Energy would complement the existing businesses of three subsidiaries in the energy space through power generation, transmission, distribution and energy storage as well as electric retail and wholesaling.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
The electric retail space in Japan has also been deregulated, leading to hundreds of participants registering to join a market that still remains in its infancy but is hope could lead to wider adoption of renewable energy. The country has a target of sourcing between 22% and 24% of its energy from renewable sources by 2030. One of the incumbent electric utilities, Tokyo Electric Power, recently announced a partnership with manufacturer Itochu to integrate its solar-based electricity retail subsidiary’s offerings with batteries.
Partnership to leverage pair’s scale, reach and technologies
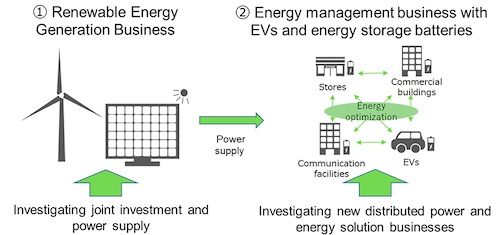
Meanwhile the Mitsubishi Corporation said today that it was seeking to expand its interests in the energy business beyond power distribution networks to “provide customers with new, value-added solutions to balance supply and demand,” through the combination of green energy sources with digital technologies.
Leveraging Mitsubishi’s existing business lines, including energy storage for industrial and vehicle use, with NTT Anode’s proprietary ICT and direct-current (DC) technologies, the pair want to combine their efforts and optimise the use of distributed energy sources “such as storage batteries and power generation facilities driven by renewables,” Mitsubishi said.
The alliance will study the prospects for jointly investing in renewable energy projects both domestically and internationally as well as using those projects to power NTT facilities. It will also build a microgrid platform to create business models involving electric vehicles and battery storage and investigate how to leverage those solutions along with the two’s existing business lines to “investigate unique energy solutions”.
The partnership will work across the downstream value chain in the battery storage sector: Mitsubishi-owned convenience stores in Japan, NTT communications buildings as well as local government facilities could get battery storage installed, serving as both backup power and energy management resources.
The pair will also investigate the applications of technologies made by third-parties, including a cloud-based system for monitoring the residual value of batteries during their lifetime in the field, made by German engineering company Bosch and the Kaluza flexibility platform for optimising distributed energy resources including EVs and storage, made by UK provider OVO Energy – in which Mitsubishi is an investor.
The news follows on the heels of fellow Japanese company NEC exiting the energy storage business this year, closing down its Massachusetts-headquartered Energy Solutions division, which had been responsible for activities in that area. Incidentally, NTT confirmed a few days ago that it is collaborating with NEC on developing “cutting-edge” technologies in the area of optical and wireless communications infrastructure.





