Japanese trading house Itochu has invested £5 million (US$7.04 million) into UK-based energy storage and related services provider Moixa, which will enable Itochu to add Moixa’s ‘GridShare’ aggregation platform to its own suite of battery storage solutions.
Less than a year after securing £500,000 of investment from major utility TEPCO, the latest funding will aid Moixa’s international expansion, not least in Japan where it will be able to launch GridShare to the battery market.
Meanwhile Itochu will promote the platform, which uses artificial intelligence to optimise the performance of their battery based on their patterns of behaviour, the weather conditions and market prices, as well as adding it to its own Smart Star battery systems.
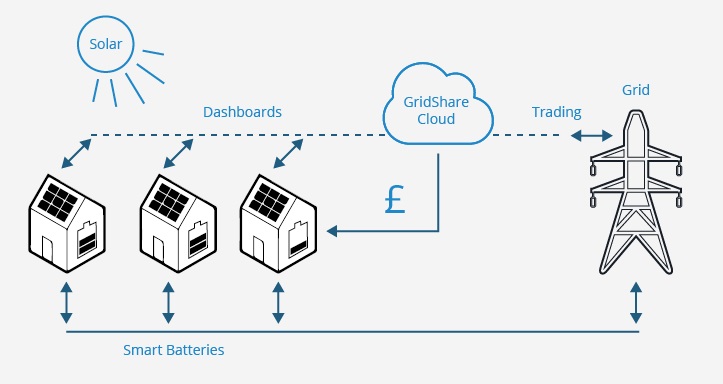
Since entering the residential energy storage market in 2013, over 6,000 9.8kWh Smart Star units – equivalent to around equivalent to 55MWh – are expected to be sold in Japan by the end of March 2018. Itochu will then install GridShare as standard on its products by the summer of 2018. In the UK, Moixa is using the platform to aggregate the capacity of multiple distributed batteries to be able to provide grid services, including lowering peak demand on local networks. System hosts or owners are paid a fee annually by Moixa for allowing the provider to use ‘spare capacity’ in their batteries to provide these services and earn revenues.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
Koji Hasegawa, general manager of the industrial chemicals department at Itochu, said: “Moixa has pioneered battery management, and we are proud to be investing and working together to target the rapidly growing energy storage market in Japan.
“Moixa’s GridShare will help our customers get more value for their home batteries and will offer solutions to help our partners manage Japan’s low-carbon transition.”
The British battery firm, which recently secured £250,000 from the UK government to expand GridShare to include aggregation of third party units for the first time, will now seek to expand its partnerships with Japanese utilities and electric vehicle manufacturers, and to market services to electricity networks.
In Japan, the 10-year period for the solar feed-in-tariff scheme will begin to expire in 2019. This is expected to lead to an increase in self-consumption of power that is generated using solar systems and energy storage systems, as one Japanese company, Solar Frontier, told Energy-Storage.News in 2016. From 2020, all new Japanese homes are also expected to be required to meet net zero or zero energy standards, something which could have a strong impact on uptake of batteries at household level in a country where the majority of people still buy a plot of land on which to build their own home, as opposed to moving into recently-vacated exsiting residences.
Simon Daniel, chief executive of Moixa, said: “Itochu is a major player in the global battery market and this partnership provides a real opportunity for us to expand our business in Japan and provide GridShare technology to many global battery companies.”
The company is also planning trials in the US and Europe this year.
While Japan has several large manufacturers of lithium batteries headquartered in the country, including Panasonic and Sony, Japan’s government and its major utilities, which currently also oversee the regional electrical grid network, have been looking abroad in recent months for energy storage providers with new or innovative business models and technologies. In addition to the TEPCO and latterly Itochu investments into Moixa, Japan’s government Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) and Mitsui are currently running a project to create a ‘virtual power plant’ of aggregated behind-the-meter energy storage systems using technology from US provider Stem Inc.