The North American Electric Reliability Corporation’s (NERC’s) 2025 State of Reliability report finds evidence suggesting battery energy storage systems (BESS) can improve primary frequency response.
NERC is a non-profit international regulatory agency that ensures the reliability and security of North America’s bulk power system. Originally founded in 1968 as the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT), NERC subsequently expanded its reach to the entire continent.
NERC establishes and enforces mandatory reliability standards for the bulk power system, encompassing transmission facilities and generators exceeding 100 MW in capacity.
Additionally, it conducts assessments to maintain compliance with these standards while also working with other organisations to tackle emergencies or threats to the power system.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
The agency should not be mistaken for the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), an independent agency of the United States government that mainly oversees the interstate transmission of electricity, natural gas, and oil.
FERC oversees the wholesale electricity market, ensuring that electricity transmission and sale rates are fair and reasonable. It also holds the power to investigate and settle disputes among utilities and other entities.
NERC analysis of frequency response
The State of Reliability report from NERC is an analysis of the performance of the bulk power system, identifying performance trends, emerging reliability risks and reporting on the relative health of the interconnected system.
The report notes that BESS in the Texas and Western interconnections “are contributing to improvements in frequency control and frequency response.”
North America’s bulk electric system (BES) operates at a nominal frequency of 60Hz. Sudden imbalances cause the frequency to change, and if it changes too much, it can damage equipment or trigger blackouts.
In Texas, an increasing number of BESS are being installed, and NERC notes that BESS installations are becoming a key part of ERCOT’s ancillary service market, providing frequency regulation services among other benefits.
The agency notes that in 2024, there were multiple instances of batteries providing 100% of the total capacity for frequency regulation services in ERCOT.
The report continues: “There was an upward trend in frequency responsive capacity for the total generation fleet from 2021 to 2024, as more generators had extra capacity to respond to a frequency event. Conversely, over the same period, this extra capacity decreased for conventional generation with the difference primarily being BESS.”
Further, NERC says that when analysing individual frequency disturbances, BESS have provided more than 70% of the overall MW response.
Severe weather findings
NERC also found that in 2024, the bulk power system (BPS) remained reliable, but the most severe outages were caused by severe weather.
“Based on the severity risk index (SRI), transmission and generation measures, and external sources, severe weather continued to represent the greatest threat to the BPS. In 2024, 27 events occurred in the United States and 3 in Canada, with losses exceeding US$1 billion within the BPS footprint; 10 of these events had notable impacts on the BES, based on the SRI.”
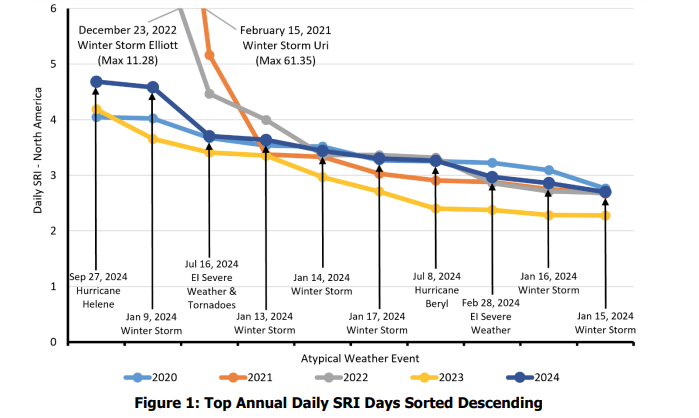
The agency acknowledged that although severe storms were the primary events affecting the BPS, they did not result in any operator-initiated load shedding. The sole occurrence of operator-initiated load shedding in 2024 was due to a failed dispatch after an unexpected generator outage in Wisconsin.
Data centre challenges
From the NERC report, “The size and speed at which data centres are being connected to and operated on the BES is creating one of the greatest near-term reliability challenges.”
The agency notes that in 2024, approximately 1,500 MW of data centres disconnected simultaneously and unexpectedly from the BES due to a transmission line fault.
A load loss of this magnitude is similar to a large nuclear power plant suddenly starting up, which causes an imbalance because of excess generation in the system.
Additionally, data centres create challenges because of the speed at which they are being built. Rather than planning for gradual load increases, more rapid adjustments must be made to adapt load forecasting, system planning and interconnection procedures.
The agency recommends implementing more protection for possible system impacts to the BPS and that grid operators and planners collect more data to understand better the risks of connecting such a large load to a system.
NERC’s full assessment can be found here.





