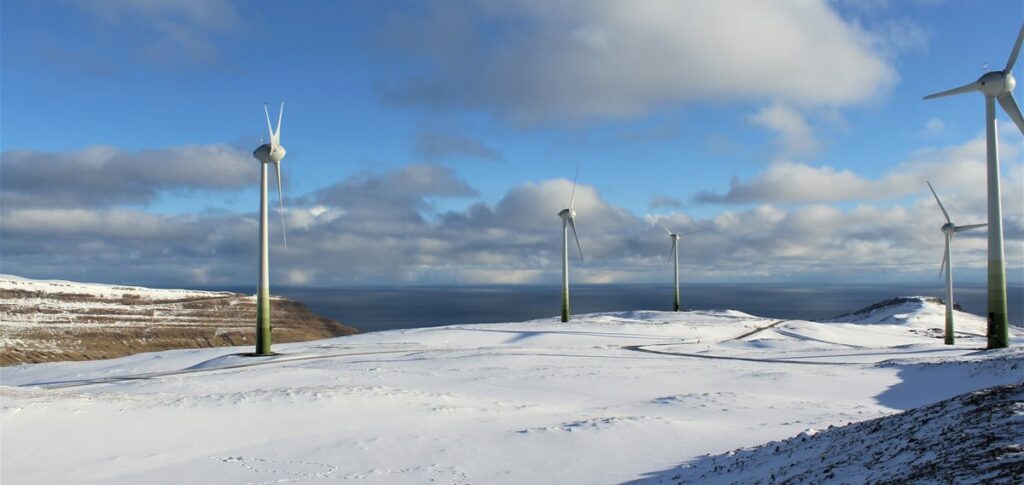
Hitachi Energy has been selected to supply a large-scale battery energy storage system (BESS) for a wind farm in the Faroe Islands, as the remote archipelago targets a goal of 100% renewable energy.
The North Atlantic islands, between Norway and Iceland and north of Scotland, are home to about 50,000 people. Without interconnection to any major grid networks, the islands are compelled to be self-sufficient when it comes to electricity generation.
Hitachi Energy said yesterday that it was contracted by the Faroese utility company SEV to supply a 6MW / 7.5MWh BESS, which will integrate a 6.3MW wind farm onto the local grid at the Faroe’s southernmost island, Suðuroy.
The project is expected to be used by the utility to assess how wind energy in combination with energy storage could be used to achieve the renewables target — which is one held by the utility, owned by the inhabitants of the self-governing Danish islands.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
SEV’s profits from selling electricity are “mostly spent on future extensions and work on the power supply units and the power supply system,” CEO Hakun Djurhuus said.
“In this way everybody makes use of SEV’s profit, and SEV can keep on developing and supplying for the growing demand of electricity.”
It already reached 49% renewables as a proportion of total power generation in 2018. Battery storage will allow the islands to maximise the use of the wind resources and add reliability and resiliency.
In the case of the Hitachi Energy project specifically, the battery system is sized at close to the total output capacity of the wind farm in order to be able to back up the local network if wind production tails off or otherwise is unable to be used.
Diesel backup systems will remain in place, but the combination of wind and battery should drastically reduce their runtime as well as the amount of fuel required to be imported. The BESS will also be able to black start the diesel generators and island the grid when the wind power covers local demand completely.
‘Innovative solutions to harness abundant resources’
Hitachi Energy said in a release yesterday that the region’s extremely harsh wind conditions make it a challenge to capture wind energy effectively and can cause operational difficulty for turbines, hence the need to back them up with generators, or now, with storage.
“SEV is at the forefront of using innovative technology in the drive toward sustainability and clean power development, even in a highly complex environment. By harnessing its abundant energy sources including wind, hydro power and solar, SEV’s network strategy not only achieves present goals, but also protects the area’s vital resources for future generations,” Hitachi Energy’s executive VP and managing director of Grid Automation Massimo Danieli said.
The Switzerland-based subsidiary of the Japanese technology conglomerate will supply its e-mesh PowerStorage BESS solutions equipment. The company has been selling and integrating the systems for some years, but under Hitachi Energy’s predecessor brand, Hitachi ABB Power Grids, before Hitachi Energy was launched this October, followed by a launch of a range of updated hardware, software and services in November including modular and inegrated battery storage solutions.
The BESS equipment to be supplied for SEV includes the PowerStore battery hardware as well as the Hitachi Energy e-mesh digital software controls and management platform, which the company can adapt to any type of distributed energy generation asset.
A few days ago, Energy-Storage.news reported that Hitachi Energy had been awarded a 35MW BESS project in Australia’s Northern Territory (NT), which will enhance the reliability of the local Darwin-Katherine electricity grid while helping integrate growing shares of renewables, particularly local rooftop solar PV. The project is a key part of the NT government’s own targeted goal of reaching 50% renewables by 2030.