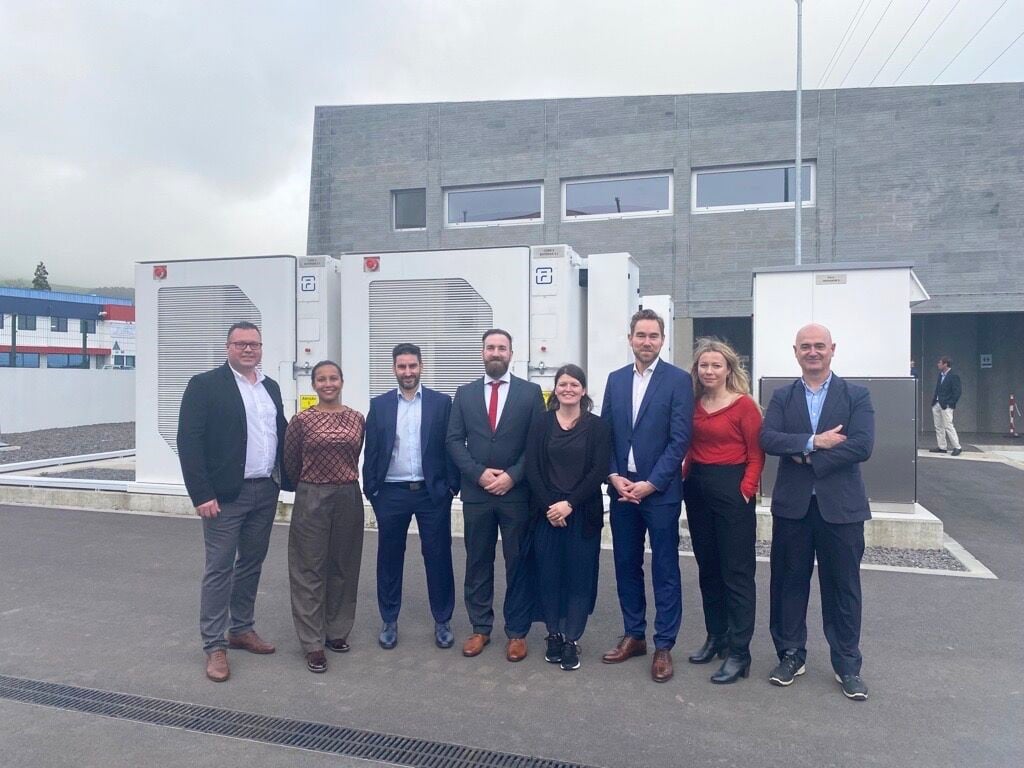
Energy storage technology provider Fluence and Siemens Smart Infrastructure have completed a renewable energy microgrid project on Terceira, a Portuguese Azores island.
Sitting in the North Atlantic Ocean a two-and-a-half-hour flight from Portugal’s capital, Lisbon, far from any of Europe’s major grid infrastructure, Terceira hosts an autonomous energy network, one of nine in the Azores.
The islands have great potential to be powered by renewable energy sources, particularly wind, hydroelectric power and geothermal energy. The project on Terceira uses Fluence’s sixth generation battery storage solution, Gridstack, and Siemens’ smart energy controls software, to help integrate renewables for utility Electricidade dos Açores (EDA).
Fluence supplied a 15MW/15MWh battery energy storage system (BESS), and with the addition of a further 6MW of renewable energy, Terceira can more than double its share of renewables on its grid to 60%.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
Siemens Power Technologies International’s (PTI) consulting team worked with utility EDA from 2018 to model the optimal BESS sizing and integration options against metrics including cost, viability, and technical requirements.
At the heart of the project lies Siemens’ Spectrum Power Microgrid Management System (MGMS), which manages the interaction between the island’s power generation infrastructure, the BESS and the island’s power consumption.
It does this through real-time monitoring and control of associated infrastructure, as well as providing forecasts of production, consumption and storage of energy over hourly or daily periods, feeding in data such as weather forecasts and historical energy consumption data.
An inauguration event was held yesterday to officially hand over the microgrid, attended by guests and dignitaries including Azores president José Manuel Bolieiro and EDA CEO Nuno Pimentel.
“This project is an important step towards a sustainable future for Terceira island and the Azores. The project allows us to better address the instability caused by fluctuating renewable resources like wind energy and can replace the diesel spinning reserve needed to cope with the challenges of maintaining grid stability and the power quality requirements of an isolated system like ours at all times,” Pimentel said.
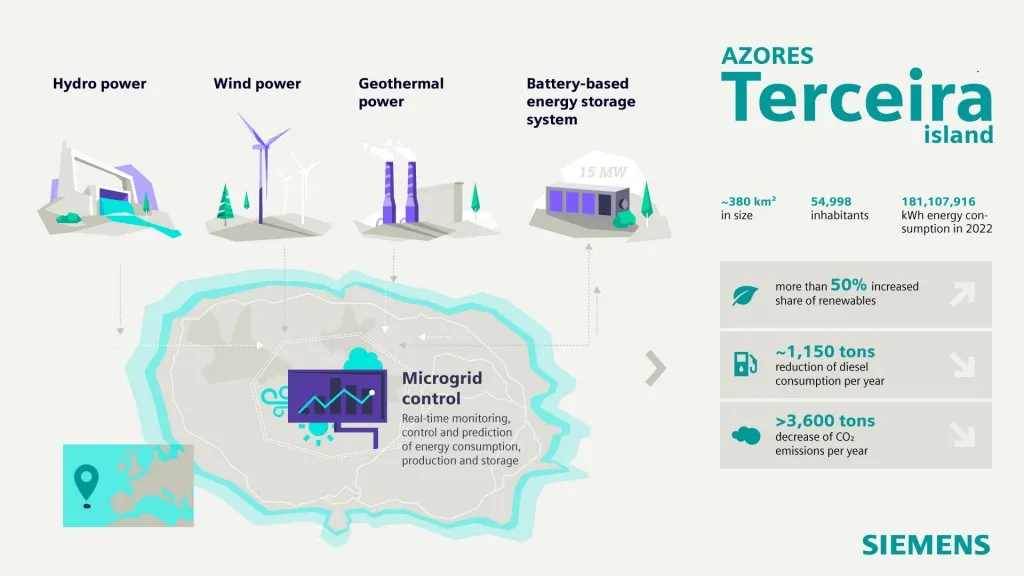
A source close to the project explained how the project’s battery storage system will reduce emissions on the island, firstly by storing excess energy produced from renewables and feeding it back into the grid at times of peak consumption or low renewables production.
It can also support the island’s grid more broadly, by leveraging renewables to provide frequency regulation and voltage balancing ancillary services, as well as N-1 contingency to the network, which allows the microgrid system to instantly pick up the load if thermal generators trip.
That means EDA can reduce its use of thermal dispatch in the form of diesel engine reserves to manage the system’s balance of supply and demand, even at times when the supply of renewable energy is low.
For Fluence, the project builds on the company’s experiences of island grids, including its successful delivery last year of a similarly-sized BESS to another Portuguese island, Madeira, for that region’s public utility Empresa de Electricidade da Madeira (EEM).
That project was also delivered in partnership with Siemens Smart Infrastructure. It is perhaps worth noting that Fluence was originally formed as a joint venture (JV) between German engineering company Siemens and US power solutions company AES Corporation. While both companies retain a stake in Fluence, launched in 2018, a stake in the energy storage company is also now owned by Qatari sovereign wealth fund Qatar Investment Authority, and went publicly listed a while back, releasing its most recent financial results in February.
“The project in the Azores demonstrates how to steadily expand renewables and integrate them into the power grid while reducing dependencies on fossil fuels and lowering CO2 emissions,” Siemens Grid Software CEO Sabine Erlinghagen said.
“Expertise in connecting software and hardware plays a central role in the energy transition.”
Read more of Energy-Storage.news coverage of island renewable energy projects with energy storage here.