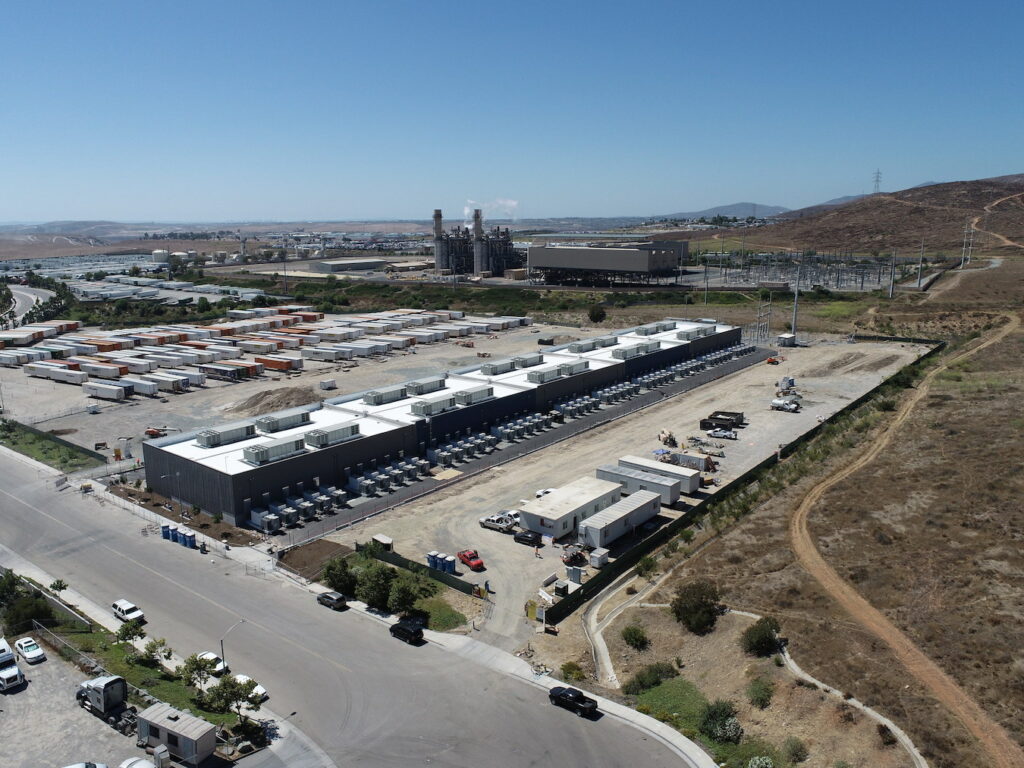

The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) has approved 497MW of energy storage procured by utility Southern California Edison (SCE) to come online from August 2023 through June 2024.
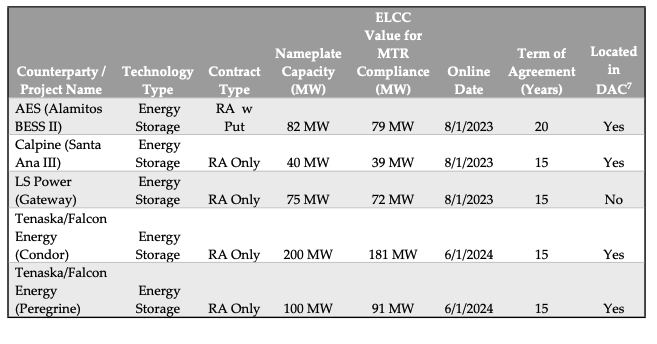
The CPUC, the state’s energy regulator, has approved five contracts for battery energy storage systems (BESS) that total 497MW of nameplate power and 1,988MWh of energy, each being a four-hour duration system.
The standalone lithium-ion BESS projects were procured by SCE under 15-20-year agreements through a ‘Fast Track’ process to ensure they are online by the aforementioned dates. See a table of all five below, which are a mix of new BESS projects and expansions to existing sites, like LS Power’s 250MW/250MWh Gateway, which was the largest in the world when it went online in August 2020 although has since been surpassed.
The five systems’ Effective Load Carrying Capability (ELCC) is slightly lower at 462MW. In CPUC/CAISO nomenclature, ELCC is a measure of the amount of equivalent perfect capacity that can be provided by an energy-limited resource such as storage.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
The five BESS projects will contribute to SCE’s portion of the 11,500MW of clean energy capacity that the CPUC last summer ordered the state’s three big investor-owned utilities (IOUs) to procure for delivery between 2023 and 2026. The other two are SDG&E and PG&E.
Commissioner Genevieve Shiroma commented: “The 500 MW of storage we approved today, fast tracked by SCE, will significantly enhance our ability to manage reliability at net peak. These five energy storage projects are essential for our path to being less reliant on fossil fuels.”
BESS’ activity in the CAISO market
As Energy-Storage.news reported today in a separate article, CAISO passed 3GW of BESS connected to its grid in April this year. Those units are now load shifting as much as 6GWh of energy a day from earlier low-demand, low-price periods of the day peak demand, high price times of the day, though this is primarily gas-generated energy rather than renewables.
Buying and selling energy in the market is now the primary function of BESS projects in the state, whose frequency regulation market is small compared to the amount of storage it now has. Utilities use BESS units to provide energy to customers in line with resource adequacy (RA) requirements, CAISO’s means of ensuring load-bearing entities like utilities have enough energy to meet demand at any time (with a reserve margin).
Four of the five contracts approved today are RA-only contracts while AES Alamitos II has a ‘put option’ too. The four RA-only contracts mean the project developers have full control and responsibility for the BESS’ dispatch into the CAISO markets and only sells as much energy to SCE as it needs to fulfil its RA requirements. With the put option, AES can ‘put’ the dispatch and scheduling rights to SCE for a pre-set $/kW-month increment to the contract’s capacity price (explained in more detail in this CPUC document).
SDG&E targets BESS investments
In related news, fellow California IOU SDG&E recently filed its 2024-27 budget proposal to the CPUC, which contained several planned investments into energy storage. It said it will put money into modernising the electric grid with various technologies to enable the integration of renewable energy, including energy storage and EV charging infrastructure.
It also wants to install more utility-scale BESS projects at strategic locations to maximise the use of solar PV-generated energy and maintain a more reliable service to customers, as well as upgrade microgrids with BESS units.





