
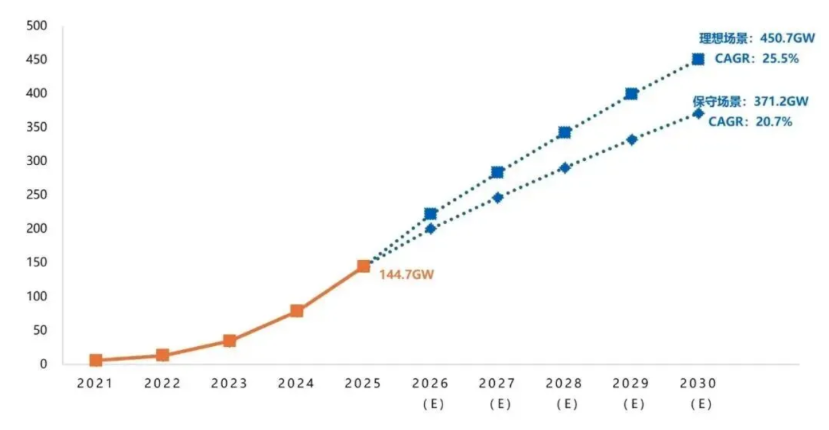
By the end of December 2025, China’s cumulative installed capacity of new energy storage technologies including lithium-ion reached 144.7GW, representing an 85% year-on-year rise.
The figures are taken from the recently released 2025 China Energy Storage Industry Data Report published by CNESA DataLink, the market intelligence arm of the China Energy Storage Alliance (CNESA) trade group.
According to partial estimates from the institution, by the end of December 2025, China’s cumulative installed storage capacity had reached 213.3GW, up 54% year-on-year.
‘New’ energy storage in CNESA’s terminology means lithium-ion batteries and other more recently-scaled technologies. ‘All’ energy storage capacity meanwhile includes pumped hydro energy storage (PHES), which has been deployed at-scale globally for several decades.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
CNESA DataLink noted that the market share of different domestic energy storage technology routes shifted in 2025, with pumped hydro storage making up 31.3% of the total figure.
New energy storage, spearheaded by lithium-ion batteries, has seen breakthrough expansion. It now holds a dominant share (exceeding two-thirds) of the total installed capacity and is rapidly diversifying beyond a single technology.
“In 2025, China’s deployments of new energy storage reached 66.43GW/189.48GWh, with power and energy capacity increasing by 52% and 73% year-on-year respectively,” disclosed Chen Haisheng, chairman of the China Energy Storage Alliance, at a conference to launch the report.
Meanwhile, the application landscape has undergone notable changes. China’s new energy storage sector has evolved from a user-side focus (35%) to being led by independent energy storage projects (58%). Frequency regulation for thermal power storage (1.4%) and the user-side segment (8%) have seen a sharp drop in their market shares. The proportion of new energy storage paired with renewable energy facilities remains steady.
In 2025, the top 10 regions in China for newly commissioned new energy storage projects were Inner Mongolia, Xinjiang, Hebei, Yunnan, Gansu, Shandong, Jiangsu, Ningxia, Qingdao and Guangdong. Each of these regions boasted an installed capacity of over 5GWh, with their combined installed capacity making up nearly 90% of the national total.
In terms of storage duration, CNESA data shows that the average discharge duration of China’s cumulative commissioned new energy storage capacity trended steadily upward from 2021 to 2025, rising from 2.11 to 2.58 hours. From 2026 onwards, the increase in duration is projected to accelerate significantly, reaching an estimated 3.47 hours by 2030.
“Looking ahead to the next five years, the new energy storage industry will see multi-faceted development across policy, technology, scale and business models,” Chen noted. Commercial and industrial (C&I) energy storage will continue its steady growth, with its revenue streams growing increasingly diversified – shifting from a single model of fixed-price spread arbitrage to a combined model of volatile market price arbitrage + demand side management + demand response (DR).
In terms of installed capacity, historical data reveals that China’s new energy storage sector has entered a phase of rapid expansion (see figure). Over the past five years, the cumulative installed capacity of China’s new energy storage has surged more than 40-fold. As the market base expands, a slowdown in industry growth has become inevitable.
CNESA predicts that the industry will move from its initial explosive growth into a phase of growth rate adjustment. From 2026 to 2030, the compound annual growth rates (CAGR) will stand at approximately 20.7% under a conservative scenario and 25.5% under an optimistic scenario. This indicates that although the growth rate has moderated, the absolute increase remains substantial. The industry is moving toward high-quality development, shifting from a policy-driven model to a market-driven one.





