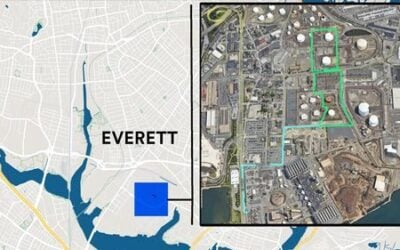
A 450MW wind-plus-storage project in Tasmania, featuring a BESS with a capacity of 200-400MWh, has been submitted for approval under the Australian government’s Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation (EPBC) Act.
The project, being pursued by developer Goldwind Australia, said the project would connect to the National Electricity Market (NEM) via access to TasNetworks’ 220kV overhead powerline.
Dubbed the Bashan Wind Farm, it is being proposed for the Central Highlands region of Tasmania, an area famed for having the state’s first hydroelectric power station at Waddamana. The project would include 56 wind turbines and three substations.
In planning documents supplied in the EPBC application, the developer confirmed that the battery energy storage system (BESS) design will be guided by the scale of storage required for the project, as well as system requirements, available technology, reliability and commercial aspects.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
It is anticipated that the facility could be located near one of the substations or comprise multiple small BESS connected to all. It could also be a subset of wind turbines and located on the turbine hardstand.
It should also be noted that the project is situated on land within the candidate Central Highlands Renewable Energy Zone (REZ) and is considered suitable for the co-location of renewable energy projects. REZs are each deemed critical infrastructure projects, coupling transmission infrastructure with large-scale energy generation, such as solar PV and wind, alongside energy storage capabilities. The Energy Corporation of NSW (EnergyCo) describes them as the “modern-day equivalent of power stations”.
Readers of Energy-Storage.news may be aware that Tasmania is already 100% self-sufficient in renewable electricity generation and has been net zero in six out of the last seven years. Most of the state’s renewable energy comes from hydro generation but is complemented by significant contributions from Tasmanian wind farms.
These often benefit from the ‘Roaring Forties’, an area of the globe that continuously sees strong winds of around 15 to 30 knots all year round. As such, an opportunity may be in place for co-located BESS to capture this energy for exportation to the grid at times of peak demand.
Wind-plus-storage developments in Australia
Several wind-plus-storage developments have captured the attention in recent months, alongside the numerous solar-plus-storage sites in Australia.
One such project is being pursued by developer Squadron Energy in New South Wales. The 700MW wind farm, featuring a co-located 400MW/1,800MWh BESS, is located west of Gulgong and northeast of Wellington in the Central-West Orana REZ, which recently first to transition into the delivery phase.
Alongside this, Swedish developer OX2 recently acquired a proposed 1GW onshore wind farm in Western Australia, including plans for a 100MW co-located BESS.
The onshore wind farm, situated north of the state capital, Perth, is still in the early stages of its development cycle. OX2 will continue to manage the approval processes. The size of the BESS is not set in stone and could be increased or decreased throughout the development process. The developer said that the BESS will be developed before the wind farm.