The acquisition of a 60.5% stake in ENGIE EPS by Taiwan Cement Corporation (TCC) was finalised and completed earlier this week.
The deal, which was announced in April, saw the Italy-headquartered stationary storage and e-mobility solutions subsidiary of French multinational Engie taken over by TCC subsidiary Taiwan Cement Europe Holdings.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
TCC said yesterday that it bought the 60.48% stake for €17.10 with the total value of the transaction at €132 million (US$155.75 million), in line with figures announced a couple of months ago. Engie EPS, which started out under the name Electro Power Systems before its acquisition in 2018 by Engie, is now being renamed New HOrizons Ahead (NHOA) and TCC’s chairman Nelson Chang flew to Italy with his management team to convene its first board meeting.
TCC, active in a number of industries, is making a major push into the renewable and clean energy and electrification sectors. It had already installed the first grid-scale battery storage system, which provides an ancillary grid service called automated frequency control (AFC) in Taiwan, as well as the first integrated solar and wind project on the island.

What both parties get out of the deal
In a press release yesterday, TCC touted now becoming a “major player” in electric vehicle charging infrastructure as well as its newly-acquired capabilities in building large-scale battery storage systems and microgrids.
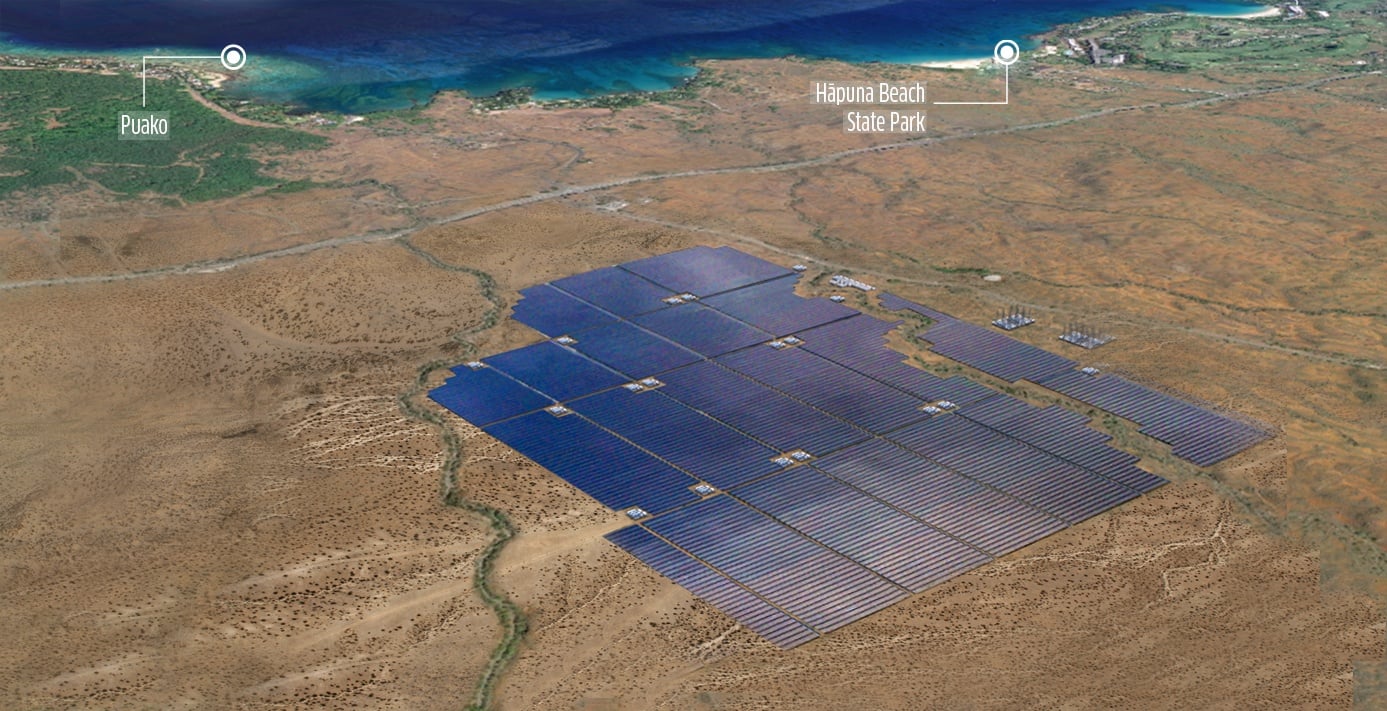
To date ENGIE EPS / NHOA has completed 300MWh of energy storage installations and has 600MWh of projects under construction, including a solar-plus-storage project in Hawaii that combines 60MWac of solar PV with 240MWh of battery storage.
Through a partnership with Free2Move, a subsidiary of automotive OEM company Stellantis, it is also deploying EV charge networks that include bi-directional vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems. Through the latter offering, the company is currently installing a 25MW V2G project in Turin, Italy, which will provide a new “ultra-rapid frequency reserve” service to Italian grid operator Terna called Fast Reserve.
ENGIE EPS CEO Carlalberto Guglielminotti and Giuseppe Artizzu, executive director for strategy and development had stated on an investors’ call back in April that the deal would give his team and customers “instant access” to a “world-class supply chain”. Guglielminotti noted that for the battery storage and high tech industries in which his company works, having a partner in Asia could open up a wide range of opportunities on both the supply and sales sides.
The energy storage company previously said it had struggled financially during 2020, which it put largely down to impacts from the COVID-19 pandemic which caused project delays and restrictions on supply chains and staff movement. It's 2020 income had been 45% less than what it made during 2019, although ENGIE EPS did say earlier this year that it expected performance to rebound in 2021 and particularly in 2022. Its 'Giga Storage and Industrial Solutions' business line, through which it delivers stationary energy storage projects, would be expected to be a major contributor in this upturn.
TCC already owns a lithium-ion battery manufacturer based in Taiwan, called E-Moli, which has 1.5GW of annual production capacity. Through this new deal it is now the sole group based in Taiwan to have in-house R&D, manufacturing and management capabilities across the value chain for clean energy and electric mobility, it claimed. The company touted NHOA’s strengths in digital software solutions, including an artificial intelligence-driven energy management system (EMS) and cloud-based monitoring platform.
TCC said immediate opportunities ahead include installing large-scale energy storage systems for Taiwan’s various big industrial players. The battery systems could reduce these entities’ peak demand use of electricity from the grid and provide backup power as needed.