A 535MW fleet of aggregated household battery storage systems, including Tesla Powerwalls, effectively reduced net load on the California grid in a recent test event.
The event took place on 29 July. During the evening peak between 7pm and 9pm, aggregators participating in virtual power plant (VPP) programmes with utilities discharged their portfolio of batteries into the CAISO grid.
The test was held in anticipation of heat waves likely to hit California in August and September, resulting in spikes in electricity demand.
Tesla, and solar and storage leasing company Sunrun, the two biggest aggregators involved in the test, commissioned consultancy The Brattle Group to analyse the findings.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
VPP participants were in all three territories of California’s investor-owned utilities (IOUs), Pacific Gas & Electric (PG&E), Southern California Edison (SCE) and San Diego Gas & Electric (SDG&E).
Most battery systems taking part were already enrolled with the state’s Demand-Side Grid Support (DSGS) load relief programme, which runs from May to October each year.
According to a source close to the VPP test, it was a “good representation of likely performance during a grid emergency,” noting similarities to how the aggregated systems performed per-site last year during a grid emergency and market-driven events.
The source said that available capacity is growing rapidly due to the accelerating adoption of residential energy storage, combined with several years of good outcomes for California VPP programmes.
Meanwhile, the intelligence behind dispatch technologies has significantly improved, resulting in yearly improvements in event preparation, dispatch performance and better forecasting of customer bill savings, the source said.
In short, customers get paid for letting the aggregator use their home battery system in the programme and the aggregator gets paid by the grid operator. Sunrun said it pays US$150 per battery per dispatching season, while Tesla is thought to have paid around US$9.9 million to VPP customers enrolled in its own aggregation programmes around the world in 2024.
“This customer-led solution is a win-win for households and the grid. Distributed home batteries are a powerful and flexible resource that reliably delivers power to the grid at a moment’s notice, benefiting all households by preventing blackouts, alleviating peak demand, and reducing extreme price spikes,” Sunrun CEO Mary Powell said.
‘Residential batteries provide dependable, planning-grade performance at scale’
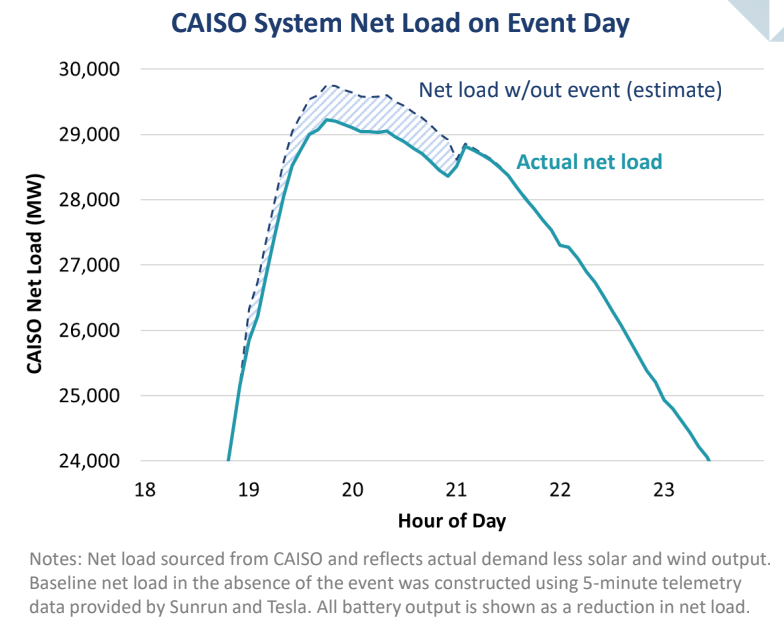
Brattle Group said the event occurred during the CAISO system’s net peak, when solar and wind generation are low, but evening demand adds load.
The firm said that the VPP’s discharging created “a visible reduction in net load” and posited that the technology could help reduce the effect of California’s famous ‘Duck Curve’.
“Performance was consistent across the event, without major fluctuations or any attrition. Events like these demonstrate to system operators that residential batteries provide dependable, planning-grade performance at scale,” Brattle Group principal Ryan Hledik said.
The role VPPs could play in mitigating CAISO’s net peak could reduce the need to invest in additional generation capacity and relieve strain on the system associated with the evening load ramp-up.
“PowerWall owners have responded to the call to create a large distributed capacity resource for California,” Tesla lead for VPPs and electricity retail, Kevin Joyce, told Energy-Storage.news.
However, at this point, the CAISO grid only calls on distributed storage systems in emergencies. The grid operator began issuing ‘Flex Alerts’ in August 2022, allowing batteries in homes to dispatch to the grid as part of the state’s Emergency Load Relief Program.
The resources quickly showed their value alongside utility-scale battery energy storage systems (BESS), helping California to avoid rolling blackouts of the kind that had occurred just two years before.
At the time, Sunrun was dispatching around 80MW of batteries to the California grid daily and Sunrun senior director of market development and policy, Chris Rauscher, said in a 2022 interview that it was unfortunate that aggregated residential batteries were only being tapped in emergency events and not to mitigate daily peaks.
The provider accounted for some 360MW of systems in the recent test, but the grid still leaves that growing resource largely untouched.
“Realising the full potential of VPPs beyond an emergency capacity use case is California’s next great challenge,” Tesla’s Kevin Joyce told Energy-Storage.news.
Joyce said Tesla looked forward to working with stakeholders including CAISO, the regulatory California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) and the California Energy Commission (CEC), “to address roadblocks and bring this timely resource to California’s capacity, energy, and ancillary services markets.”
Sunrun’s storage attachment rate for residential leases reached 70% in Q2 2025, the company said in its recent results release. During the quarter, it deployed 392MWh of batteries. Meanwhile, Tesla reported a 2% year-on-year growth in energy storage deployments, versus a 13% decrease in vehicle sales in its most recent quarterly results.





