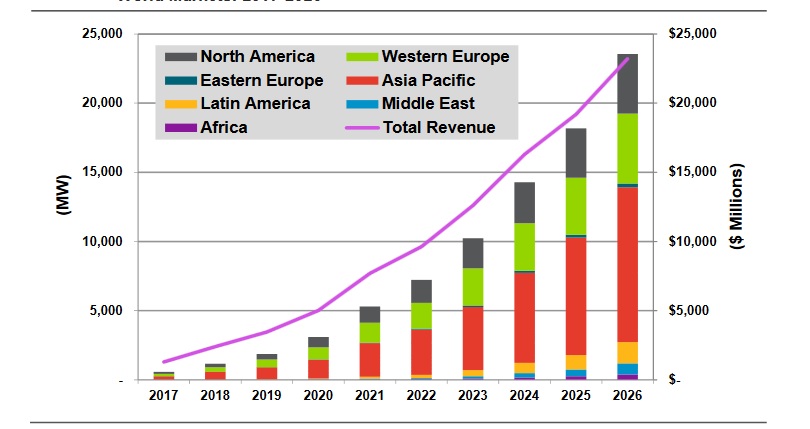
While acknowledging that the economics “vary significantly” by region and application, Navigant Research has forecast that energy storage for integration of renewables and co-located with solar or wind could be worth more than US$20 billion by 2026.
‘Energy storage for renewables integration’, a new report from the Colorado-headquartered research and analysis group, looks at the point at which the falling costs of new solar and wind generation will meet with the falling costs of lithium and other advanced batteries to converge on a ‘sweet spot’ for adding storage to generation assets.
To date, the higher value applications of batteries have been found not in their combination with solar or wind – where they could maximise self-consumption of PV or minimise the grid curtailment of wind – but in areas such as providing ancillary services to the grid like frequency response. While the huge drop in the cost of renewables has provided a driver for the addition of energy storage, the cost of the storage systems themselves still remains the biggest obstacle, authors Adam Wilson and Alex Eller said. The challenge presented in adding ever-higher shares of renewables to grids around the world means it is increasingly likely energy storage will be used as a facilitating agent.
Many factors influence the cost and suitability of energy storage for this use, including the condition, state and size of the local grid, the amount of renewable generation being added to it, local electricity rates, policies and the available options for financing. Meanwhile the industry, still in its early stages, lacks standardisation and a dearth of the aforementioned financing options, Navigant found. Complicating the picture further still is the fact that solar PV prices have dropped in some regions to the point where it would be simply uneconomical at this point to add the more expensive energy storage component.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
Navigant said that while some regions have stripped back policy support for solar PV, phasing out or removing feed-in tariffs (FiTs), leading to a corresponding drop in demand from customers behind-the-meter, even some of these regions, where electricity prices are still rising, the economic competitiveness of solar and energy storage grows. The research firm also pinpointed Australia, California, New York and Germany as solid examples of regions where policy support and rising electricity retail rates have converged to see “strong deployment” of energy storage for renewables integration (ESRI).
Asia-Pacific to rule the roost
Through to 2026, the Asia-Pacific region is likely to be the world’s leader in ESRI applications, according to the report. There could be 11.18GW of such systems deployed in the region by then, due to the existence of large renewable energy markets and a number of strained or underdeveloped grids.
Worldwide, Navigant has forecast annual revenues in the ESRI space in eight years’ time to reach US$23.201 billion. The report examined the utility-scale solar and wind-plus-storage spaces and behind-the-meter energy generation, focusing on six utility-scale, commercial and industrial (C&I) and residential applications. The authors noted that the report does not cover the microgrid or remote system markets.
Read Alex Eller from Navigant’s piece on how transmission and distribution (T&D) network operators could increasingly look to energy storage and related technologies as non-wires alternatives (NWA) to expensive infrastructure assets like substations from the latest PV Tech Power.





