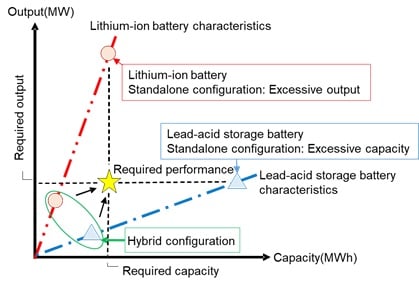
A hybrid battery energy storage project aimed at helping authorities and power system operators in Poland better understand how to integrate and expand renewable energy capacity in the country has gone into operation.
Located at the 24MW Bystra wind farm in northern Poland, the Smart Grid Demonstration Project combines high output lithium-ion batteries with high-capacity lead acid batteries that will help mitigate the fluctuating output of the wind turbines while also helping to protect the electricity network from transmission and high distribution line overload problems in the event of power grid failures.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
The system can also perform other advanced applications such as allowing for energy arbitrage, responding to shifting power demand and providing frequency reserve. Poland is expected to greatly increase its installed wind generation capacity in the coming years in line with climate plan commitments and EU directives, particularly in the wind-rich north. The project began a “monitoring phase” in June and has just begun full operation in its demonstration phase.
The start of full operations is the culmination of three years of work since Japan’s government New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organisation (NEDO) signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) in March 2017 to undertake the project with Poland’s energy ministry, also known as the Ministry of Climate.
NEDO recently supported the start of operations of what is thought to be the world's largest single-stack hydrogen electrolyser in Fukushima, Japan and is also working with northern Japanese utility company Hokkaido Electric Power to investigate how to integrate greater shares of renewables – including an increase in wind capacity – on the northern Japanese island of Hokkaido.
NEDO contracted a consortium of Japanese companies to provide technology and expertise to implement the project, namely Showa Denko Materials, which manufactured and supplied the 1MW/0.47MWh of lithium and 5MW/26.9MWh of lead acid batteries; Hitachi, which made and supplied the battery energy storage system’s distribution control system as well as Hitachi ABB Power Grids, which supplied 6MW of power conversion system (PCS) equipment.
Japanese banking company SMBC was also involved in the project from a financing angle and together with Showa Denko Materials and Hitachi will develop business models around such projects that could potentially be replicated at scale.
Along with the support of the Polish Ministry of Climate, local project partner companies were also involved, including state-owned transmission system operator Polskie Sieci Elektroenergetyczne (PSE) and electric power distribution company Energa. PSE will control the hybrid system.