Horizon Power, an electricity supplier owned by the state government of Western Australia has begun commissioning community battery storage to allow nine remote towns to use more rooftop solar power.
The AU$31 million (US$22.76 million) plan, called Energy Storage in Regional Towns, is being funded by the Western Australia (WA) government through its WA Recovery Plan. The nine systems will add more than 9MWh of battery capacity to local electricity networks.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
The battery systems will store excess solar PV generation which would otherwise be wasted and enable about 3,000 households to be able to add 3kW standard-sized solar systems to their rooftops and reducing the state’s carbon dioxide emissions as well as customer energy bills by AU$1,275 per year on average, according to Horizon Power.
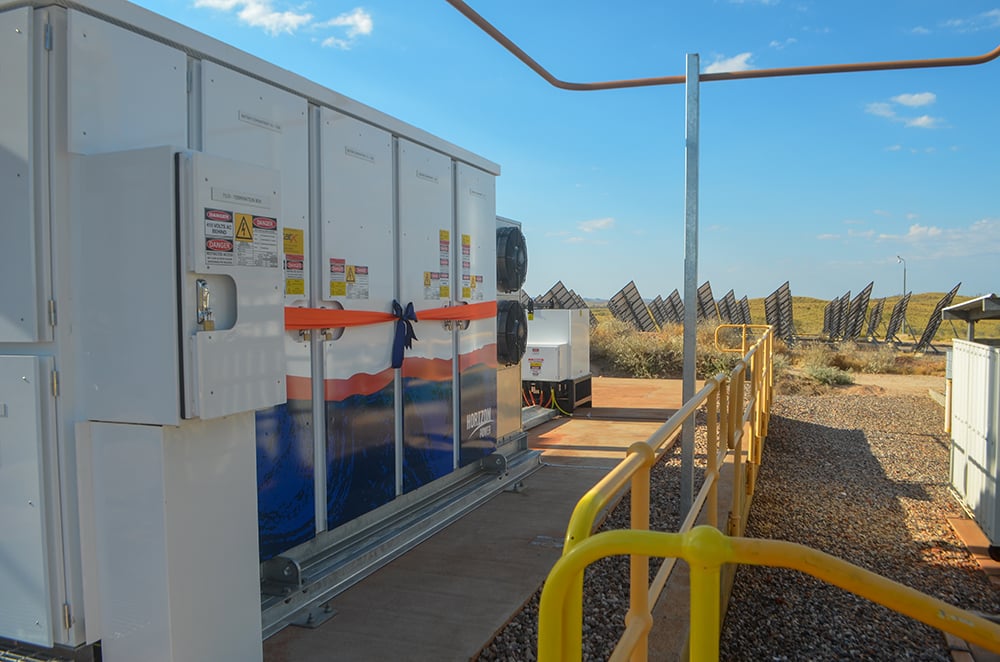
Three have already been commissioned, with a community event held last Wednesday (10 November) to commemorate the most recent. The 582kW / 583kWh battery energy storage system (BESS) at Marble Bar in the East Pilbara region of WA will free up more than 100kW of local solar hosting capacity.
Hosting capacity had been capped to preserve network stability, a Horizon Power spokesperson told Energy-Storage.news.
Marble Bar is in fact recognised in the Guinness Book of World Records as Australia’s hottest town, with temperatures in excess of 37°C sometimes recorded for over 100 consecutive days of the year. The BESS will be complementary to an existing large-scale solar farm in the town which generates more than 1GWh of power annually.
It was supplied and installed by a local renewables company, Hybrid Systems Australia, and was commissioned on 27 October 2021, the Horizon Power spokesperson told Energy-Storage.news. It is about to undergo 60 days of reliability testing and is expected to go into full service early next year.
Two other systems commissioned in the towns of Wiluna and Yalgoo, hosting 291kW / 365kWh and 194kW / 219kWh respectively, are already undergoing their reliability testing which is expected to be completed before the end of this year and also put them into service early next year.
Western Australia’s energy minister Bill Johnston welcomed the commissioning of the BESS at Marble Bar, noting that the Energy Storage for Regional Towns programme will unlock more than 10MW of extra rooftop solar capacity, which would reduce local CO2 emissions by 13,000 tonnes per year.
“The project roll-out will also support economic development, providing opportunities for local installers to supply solar systems to customers,” Johnston said.
Rest of BESS projects will be in place by end of next year
The rest of the BESS projects in the programme will be rolled out in the next few months, most of which will be completed by mid-to-late 2022 although the biggest in kilowatt-hour terms, which is at the town of Broome (4,300kW / 4,391kWh), is still in the design stage and expected to be completed in late 2022.
Horizon Power noted that additional rooftop solar PV hosting capacity is currently exhausted in most, if not all, of the regional towns selected.
Onslow, another Western Australia town in Horizon Power’s service area, hit clean energy industry headlines earlier this year when it was proven to have gone entirely fossil fuel-free for a demonstration period of an hour and 20 minutes.
The feat was achieved through the combination of 700kW rooftop and 600kW of ground mount solar PV, battery storage at customer sites and at a substation, linked together with a distributed energy resources management system (DERMS) and microgrid controls technology.
Horizon Power engineers determined the right time to disconnect Onslow from its centralised 1MW natural gas power plant. The town also has 1MW of diesel generators as backup.
Different types of ‘community’ battery energy storage systems are being installed by various energy industry and public agency actors around Australia — and in other parts of the world. In the video below, experts from the Australian National University (ANU) explain and analyse how these shared battery systems can work to the benefit of a range of stakeholders.