UK electricity system operator National Grid ESO is reviewing its previously-announced timescale for the introduction of two dynamic frequency response services and phase out of the existing market regime.
A spokesperson for National Grid ESO told our sister site Current± that it is currently “reviewing the dates and timescales” originally set out in 2019’s Response and Reserve Roadmap, due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic across Britain.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
This roadmap detailed its plans to implement Dynamic Containment – which already went live earlier this month – and Dynamic Moderation and Dynamic Regulation, with the three together set to replace firm frequency response (FFR).
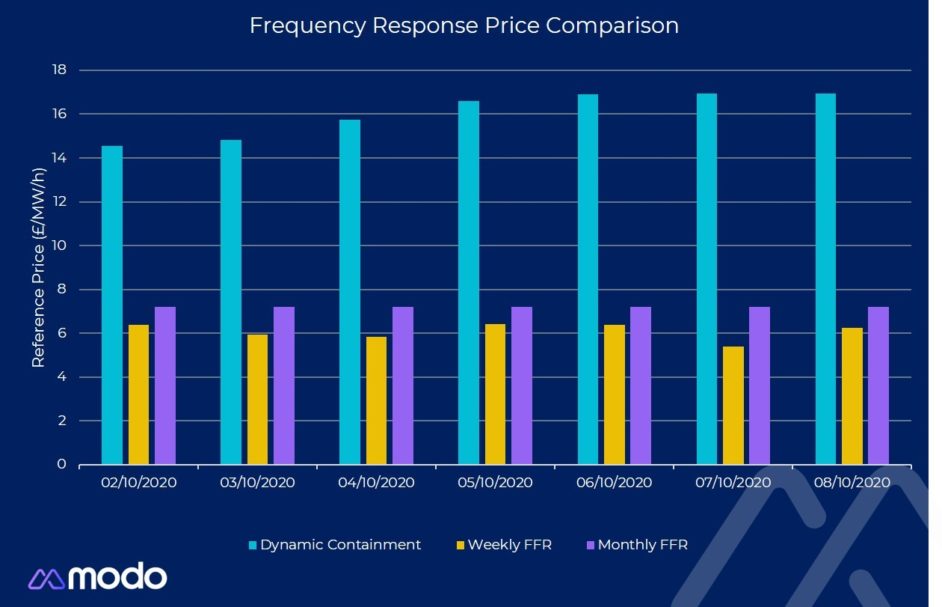
This switching from the long-established FFR to the dynamic suite could result in National Grid ESO “facing friction” from older assets that prefer the legacy service. This is according to energy transition data science company Modo Energy’s lead data scientist and market analyst Alex Done, who told Current± that as it stands prices in Dynamic Containment are “really high”, resulting in a “strong market incentive for asset to make that move”.
National Grid ESO currently operates a price cap for Dynamic Containment, with Done explaining that “with some bids being rejected for being too expensive, the market has very quickly adjusted to the fact that National Grid are willing to pay about £17/MW/h (US$22.05) for the service.”
However, despite this rejection of bids over price, there currently isn’t enough spare capacity to fill National Grid ESO’s aim of sourcing 500MW each day.
“There’s roughly 400MW in the monthly FFR and an extra 100MW in the weekly auctions. The capacity of energy storage that is providing frequency response services excluding FFR in 2020 is about 700MW, so there's only a further 150MW-200MW that can actually participate in Dynamic Containment.
“Generally speaking, one of those markets is going to be short on capacity, and at the moment it's Dynamic Containment. But the price signals that Dynamic Containment sends to the market is that participants should be moving into this auction instead of the other ones, and that is precisely what I'd expect to happen as soon as it becomes a viable option for anybody who's considering it.”
However, this then could result in challenges with metering for those switching over, with National Grid ESO requiring a live data feed of what assets are doing at 20 datapoints per second. This is “quite a challenge for older assets”, Done said, and could potentially require metering upgrades and additional investment in pre-existing sites.
Flexitricity’s chief strategy officer, Alastair Martin, also spoke to Current± about the metering data required by National Grid ESO, stating that the volume data it will need to process is “quite high for the service” and “high for the providers too”.
However, Martin praised the ESO for being “upfront with the service” and for implementing it “largely as it was presented to the market”.
Modo’s Alex Done recently blogged for Energy-storage.news just ahead of the Dynamic Containment launch, explaining what the service is, how the market will work, and what the impact is likely to be for the UK’s energy storage assets and their operators and owners. Read that full blog here. Alex also spoke to Current± this week for a Q&A explaining how the implementation has gone so far and what we might expect to see going forwards, which you can read here.
The original version of this story first appeared on Current±.