
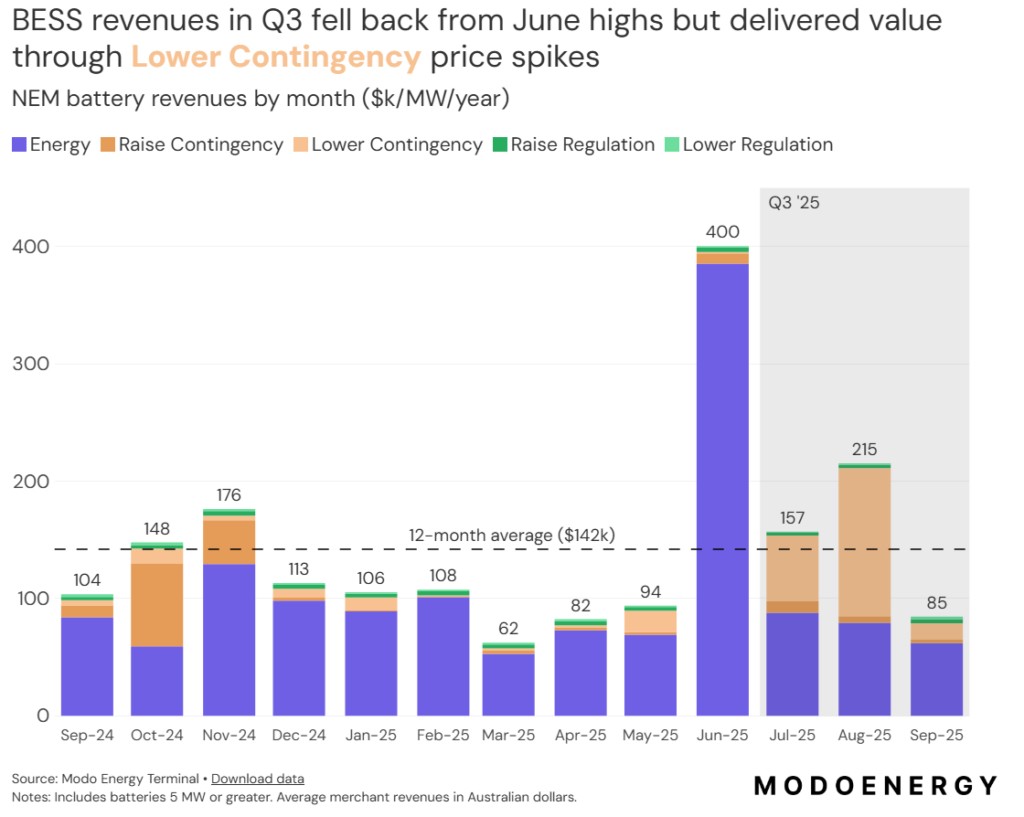
Battery energy storage revenues in Australia’s National Electricity Market (NEM) fell 61% in September 2025 to AU$85,000/MW (US$56,712/MW) as price volatility eased across the grid, according to new research from Modo Energy.
The research firm said the revenue decline continued the volatility compression that began in July, when NEM-wide battery energy storage system (BESS) net revenues averaged AU$157,000/MW per year, falling over 60% from June highs. This then increased to AU$215,000/MW per year in August before dropping to AU$85,000/MW.
Queensland emerged as the exception to the September downturn, supported by increased Frequency Control Ancillary Services (FCAS) contingency pricing that helped offset broader market softness.
South Australia maintained its position as the revenue leader during the quarter, with BESS in the state benefiting from multiple days of elevated frequency control ancillary services pricing.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
However, Modo’s research reveals that many assets across the NEM struggled to capture full value from available market opportunities, highlighting the increasing sophistication required for optimal battery dispatch strategies.
The revenue compression occurs against a backdrop of unprecedented capacity expansion in Australia’s energy storage sector.
During the quarter, Victoria became the first Australian state to cross 1GW of simultaneous battery storage charging, delivering 1,049MW in a single interval, while Australia’s NEM battery storage surpassed the 6.5GWh milestone during a record-breaking weekend in late September.
Modo Energy’s analysis projects that 12.5GW of the 16.8GW development pipeline will achieve commercial operation by the end of 2027, representing a sevenfold increase in operational battery capacity over three years.
This massive expansion is expected to fundamentally alter market dynamics, with price spreads projected to fall as BESS capacity increases across the NEM.
The research identifies New South Wales as facing the largest transformation, transitioning from the mainland state with the least battery energy storage capacity to the most.
Modo said this rapid capacity addition is expected to compress arbitrage opportunities in the near term, though thermal generation retirements will reshape the competitive landscape from 2027 onwards.
The scheduled closure of the 2.8GW Eraring coal power station in 2027 represents a critical inflection point for market dynamics. Readers of Energy-Storage.news will likely be aware that the site is being transformed into one of Australia’s largest BESS facilities, standing at 2.8GWh.
Modo projects that the retirement of the coal-fired power plant will increase volatility in New South Wales and, to a lesser degree, in South Australia and Victoria, creating new revenue opportunities for battery storage operators capable of providing flexible capacity during peak demand periods.
The growing importance of cap contracts
Modo’s research also highlights the growing importance of cap contracts as a risk management tool for NEM battery storage systems. These contracts offer increased returns while reducing revenue volatility and uncertainty.
This financial innovation demonstrates the sector’s maturation as developers seek to optimise risk-adjusted returns in an increasingly competitive environment.
Sixteen battery projects totalling 15.37GWh secured Capacity Investment Scheme Agreements (CISAs) during Australia’s largest battery auction to date in September, providing revenue certainty that supports project financing while contributing to grid reliability objectives.
These contracts underscore continued government support for energy storage deployment as Australia pursues its enhanced emissions reduction targets.
The operational data showcases the dispatch patterns as battery operators optimise revenue streams across energy arbitrage, FCAS participation, and emerging grid services.
Grid-forming technology drives additional revenue streams
Modo Energy’s analysis reveals that grid-forming battery storage systems are unlocking additional revenue opportunities beyond traditional energy arbitrage and FCAS participation.
Grid-forming inverters enable BESS to provide inertia and system strength services that become increasingly valuable as coal-fired generation retires from the NEM. These are also becoming the “new norm for BESS in the NEM”.
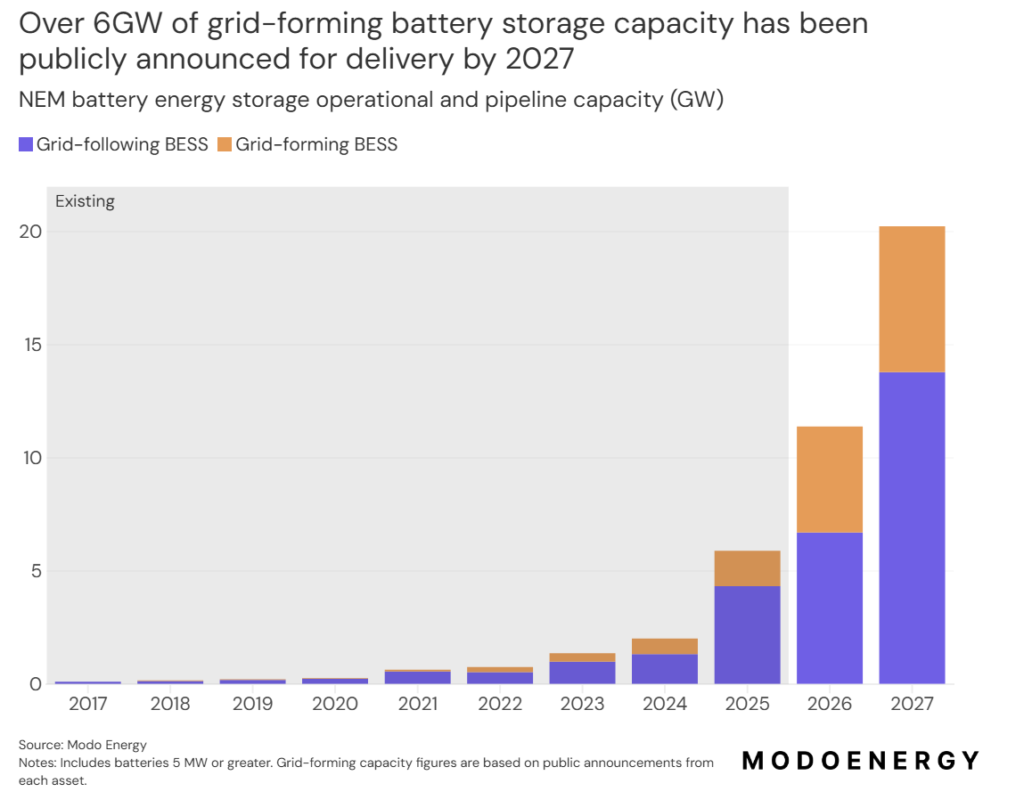
Indeed, Modo states that over 6GW of grid-forming battery storage capacity has been publicly announced for delivery by 2027.
The research indicates that grid-forming capabilities allow battery operators to avoid costly system strength charges while securing network support payments from transmission network service providers.
These additional revenue streams are becoming particularly important as the electricity system transitions toward higher renewable energy penetration and requires enhanced grid stability services.
Grid-forming battery storage systems provide essential system services by maintaining voltage and frequency stability during grid disturbances, capabilities that traditional grid-following systems cannot deliver.
As thermal generation capacity retires, these services become critical for maintaining grid reliability, creating sustained demand for grid-forming energy storage assets.
The technology represents a significant advancement in battery energy storage system capabilities, enabling assets to operate independently of the grid and provide black start services during system restoration events.
This functionality positions grid-forming BESS as essential infrastructure for grid resilience as Australia’s electricity system undergoes structural transformation.





