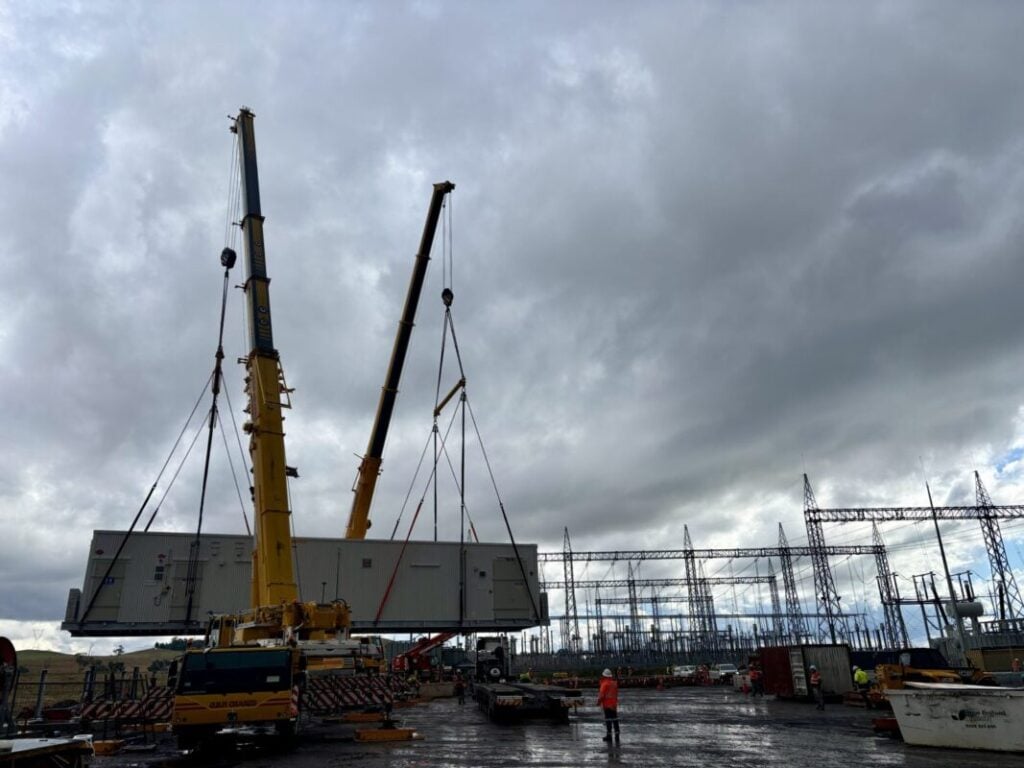
Renewable energy developer Acen Australia has submitted plans for a 440MW/1,760MWh battery energy storage system (BESS) in Queensland to Australia’s Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation (EPBC) Act.
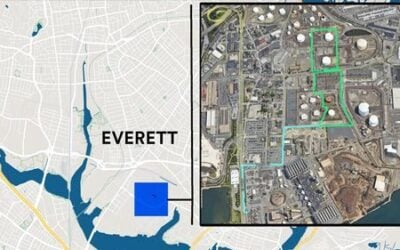
The proposed Lilyvale BESS will be located in the Central Highlands region of Queensland, approximately 52km northeast of Emerald and 800km northwest of the state capital, Brisbane.
The development will be constructed on a 151.52-hectare rural property currently used for stock grazing, with the actual disturbance footprint covering approximately 21.15 hectares.
According to the EPBC Act application, the BESS will include lithium iron phosphate (LFP) battery cells. The system will comprise 512 BESS containers, 128 inverters, and 128 medium-voltage power stations.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
Additional infrastructure includes associated electrical equipment such as primary transformers, high-voltage substations, auxiliary transformers, and harmonic filters, as well as administrative, operations, and maintenance buildings.
The BESS will connect directly to the existing Lilyvale Substation located immediately adjacent to the west of the project area via underground or overhead cables, providing efficient grid integration without requiring extensive new transmission infrastructure.
In doing so, the BESS will connect to the National Electricity Market (NEM), which spans Australia’s eastern and southern coasts and the island state of Tasmania. The Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water recently published its hugely anticipated NEM Review Draft Report.
The site is positioned approximately 3.7km northwest of the Lilyvale Solar Farm, a 126.2MW solar PV facility commissioned in March 2019. It also sits about 3.4km northeast of the Bowen Basin Coalfields and Gregory/Crinum Mine, and roughly 1km south of multiple coal mine sites, including Mancala Oaky Creek North, Oaky Creek North, and Aquila Mine.
Queensland’s growing energy storage pipeline
This proposed project joins a growing portfolio of large-scale battery systems being developed across Queensland as the state works to integrate more renewable energy into its grid.
In April 2024, the Queensland government announced construction would soon begin on Quinbrook’s ‘Supernode’ project at Brendale, featuring a 250MW/500MWh battery system. More recently, the first 270MW/540MWh stage of Neoen’s Western Downs battery near Chinchilla commenced operations, while Akaysha Energy’s 150MW/300MWh Ulinda Park BESS is expected to be operational in Q3 2025.
State-owned energy company Stanwell has also begun construction on a 1,200MWh BESS at the coal-fired Stanwell Power Station.
Earlier this year, Acen Australia secured AU$750 million in debt financing to support the rollout of its 13GW renewables and energy storage portfolio in the country.
Acen Australia managing director David Pollington welcomed the financing at the time, stating that it would create a “robust funding base for the company’s diverse portfolio of wind, solar, pumped hydro and BESS projects.
Additionally, the financing will support the ‘near-complete’ 400MW Stubbo Solar project and the 720MW New England solar PV power plant in New South Wales.
The New England plant, which is divided into two stages, saw its first stage operational in March 2023.
Our publisher, Solar Media, will host the Battery Asset Management Summit Australia 2025 on 26-27 August in Sydney. You can get 20% off your ticket using the code ESN20 at checkout.