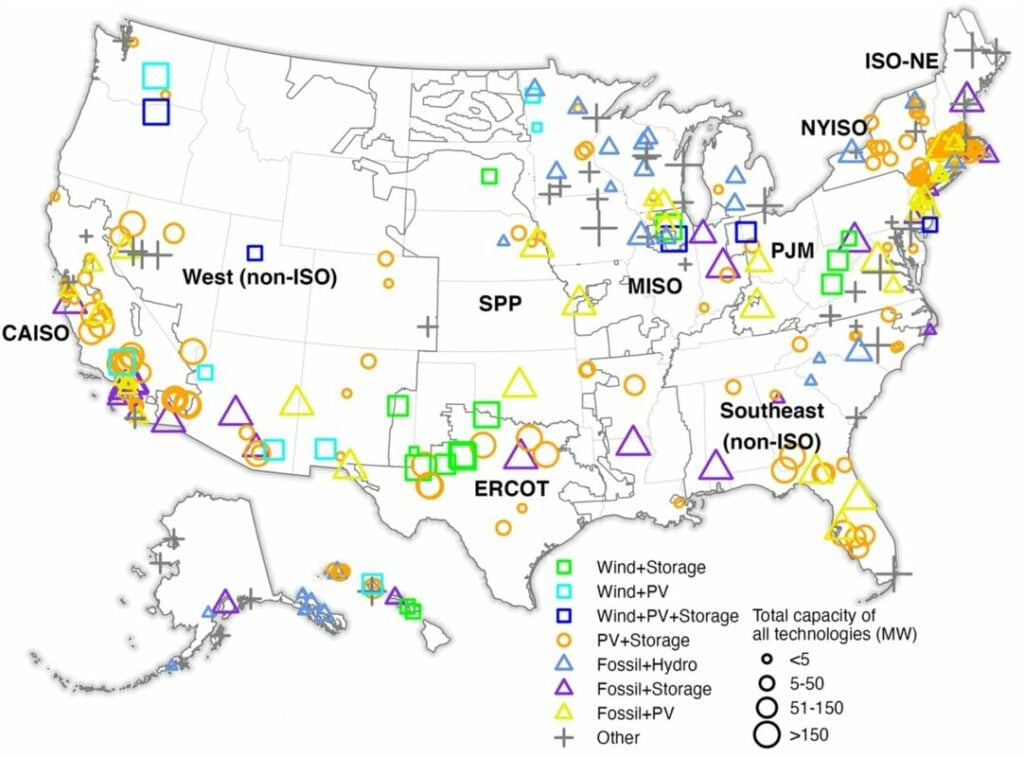
By the end of 2022, US co-located renewable and energy storage projects totalled 41GW of generating power and 5.4GW/15.2GWh of energy storage, according to Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) analysis.
The capacity is spread across 374 hybrid plants, visualised in LBNL’s map above. The 41GW represents a 15% increase in cumulative capacity versus the previous year while the energy storage capacity nearly doubled, growing 69% by GW power and 88% by GWh capacity.
The national laboratory defined hybrid plants as those combining two or more resource types, whether multiple types of generation or generation and storage, using a single point of interconnection. They don’t necessarily need to feature coordinated operations of the hybrid/co-located resources, i.e. the storage charging from the solar.
Solar PV plus storage is the most popular type of hybrid project, LBNL said, show the distribution between different combinations below.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
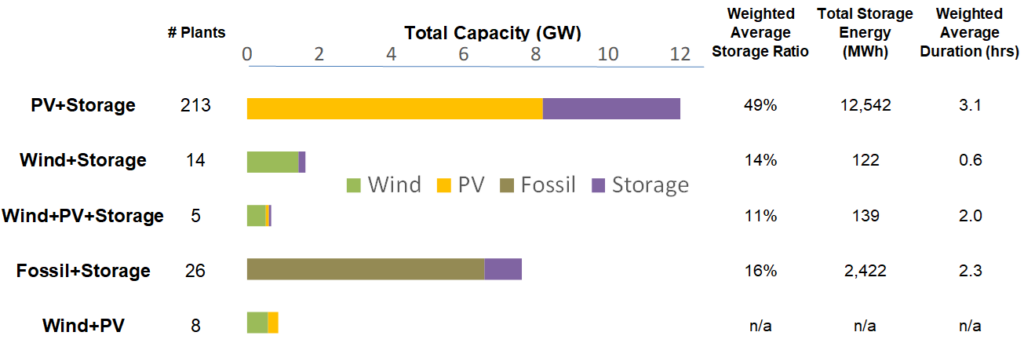
The organisation added that by GW capacity, PV-co-located and standalone storage capacity are roughly at par, around 4GW, while PV-co-located projects are larger by GWh capacity – 12.5GWh versus 10.4GWh.
It also said that its research showed that storage assets co-located with PV are mainly providing capacity firming services and energy arbitrage while those co-located with wind resources are primarily targeting the ancillary service markets.
LBNL added that it the figures in its analysis do not include the impact of the Inflation Reduction Act’s investment tax credit (ITC) for standalone energy storage, but it expected a continuing trend towards co-located projects for other reasons.
Major US co-located projects Energy-Storage.news has reported on in the last few weeks include an offshore wind proposal containing a 253MW storage option in New Jersey, a solar-plus-storage project acquisition with a 50MW battery in New Mexico, and the start of construction on another in the state with 100MW of energy storage.
Our publisher Solar Media is hosting the 10th Solar and Storage Finance USA conference, 7-8 November 2023 at the New Yorker Hotel, New York. Topics ranging from the Inflation Reduction Act to optimising asset revenues, the financing landscape in 2023 and much more will be discussed. See the official site for more details.