The developer of one of the world’s biggest battery energy storage systems (BESS) installed globally so far will be taking its vanadium redox flow systems into the international market, beginning with a pilot in Belgium.
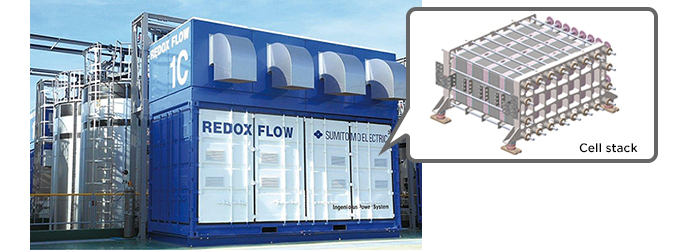
Japan’s Sumitomo Electric Industries, which put a 60MWh vanadium redox flow system into operation to assist the integration of renewables on the northern Japanese island of Hokkaido, has formed a strategic partnership with Belgium-headquartered CMI Group to market the former’s Redox Battery in international markets.
The agreement is expected to give Sumitomo better access to regions including Europe and the Middle East and North Africa (MENA). The Japanese company described CMI Group as a “European partner capable of installing their (Sumitomo’s) Redox Battery and integrating it into the balance of system”.
CMI has been established in power generation – beginning with steam engines – for about 200 years, running the CMI Energy subsidiary and now also moving in to batteries with the creation of CMI Energy Storage. The company runs engineering procurement and construction (EPC) activities in energy storage and will now include Sumitomo’s flow technology in its offerings to market.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
A pilot project will be established at CMI’s headquarters in Seraing, Belgium, where 2MWp of solar PV will be paired with about 3MWh of “various types of batteries”, scheduled to begin commercial operation in 2018. The project will trial a number of different use cases for energy storage, including self-consumption of onsite generated PV power, grid stabilisation and arbitrage.
As we have seen over the past few months at Energy-Storage.News, competition in the flow battery space, as a handful of makers race to commercialise and gain visibility in the market, is becoming fierce. Various exploration deals for raw materials and sales partnerships have been established, while in China, government support is expected to sire several flow battery systems in the range of hundreds of megawatt-hours of energy storage per system.