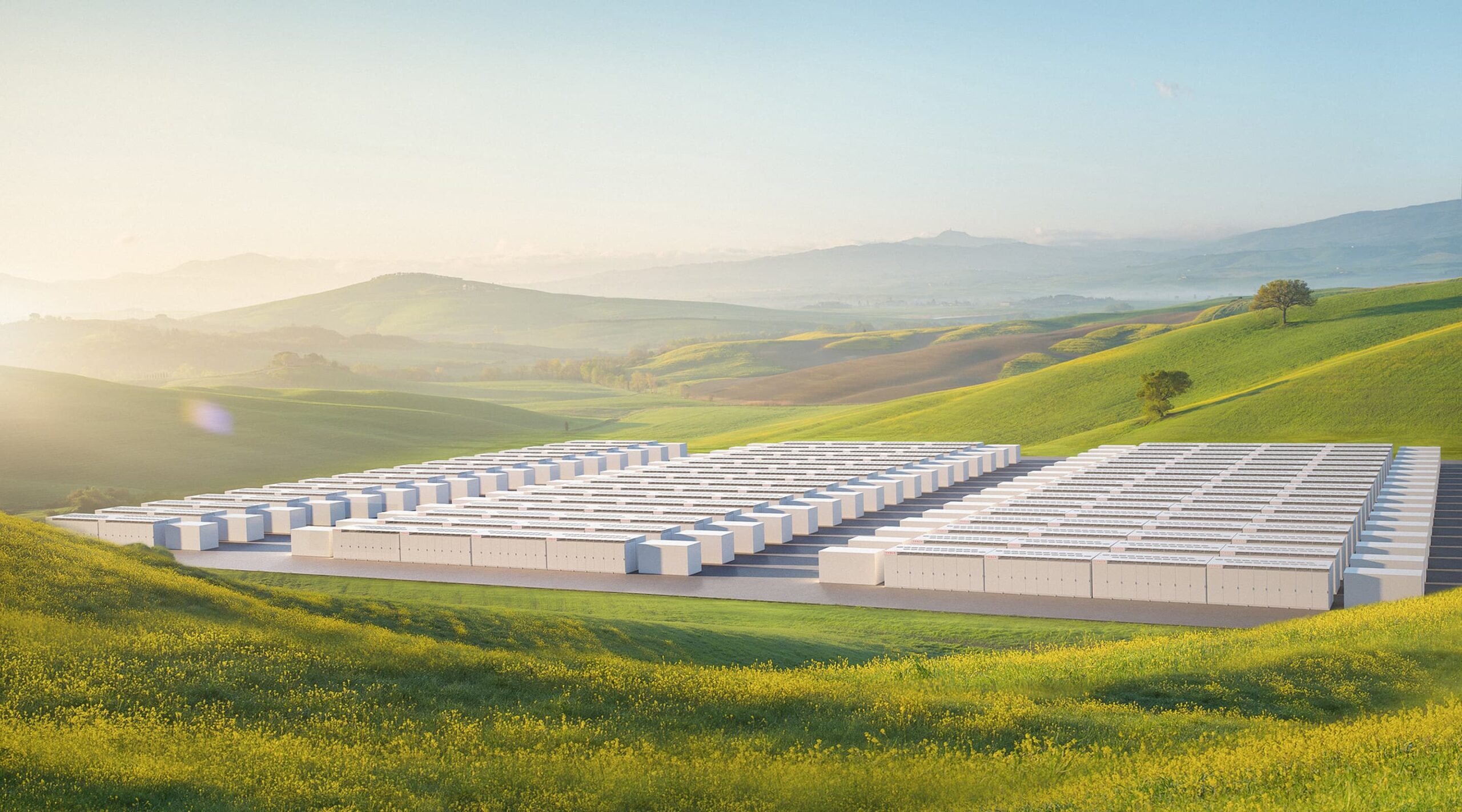
California investor-owned utility (IOU) Pacific Gas & Electric has begun work constructing a 182.5MW / 730MWh battery energy storage system (BESS) project at a substation in California.
The project, at Moss Landing substation, Monterey County, is one of four large-scale systems approved by the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) in November 2018, planned as a replacement for peaking natural gas plants by Pacific Gas & Electric (PG&E). After that the local Planning Commission for Monterey County issued its own approval in February this year.
CPUC had issued approval of three capacity contracts and one power purchase agreement (PPA) for the four projects, totalling 567.5MW and each with four hours’ duration of storage. The Moss Landing project, which is being built using battery storage equipment supplied by Tesla, is the second largest of those four, with another 300MW / 1,200MWh on its way from integrated energy company Vistra Energy and its subsidiary Dynegy.
Tesla and PG&E will design, construct and maintain the Moss Landing substation project, scheduled for completion in early 2021 and to reach full operation by the second quarter of next year. PG&E expects the BESS to save over US$100 million over its 20-year lifetime, as it helps the utility meet local capacity requirements and mitigate energy procurement costs.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
PG&E said that COVID-19 safety protocols will be met by employees and contractors, including health checks, physical distancing and the wearing of face coverings, with up to 50 staff expected onsite to construct the system, which will use 256 units of Tesla’s Megapack 3MWh battery storage systems which came onto the market last year.
PG&E and Tesla have an agreement in place that means the system’s capacity could be increased to as much as 1.1GWh in total – six hours’ storage duration at the same rated output. in addition to meeting capacity requirements, the Moss Landing BESS will also participate in transmission and distribution (T&D) operator CAISO’s markets for energy and ancillary services.
According to the utility, which is one of California’s three main IOUs, PG&E has now awarded over 1,000MW of contracts for battery energy storage projects in its service area for deployment through to 2023, including a mix of third-party-owned projects and utility-owned. There are also now around 140MW of behind-the-meter (BTM) battery systems at customer sites in PG&E’s service area.
Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems Americas awarded 20MW / 80MWh project to be used in ‘multiyear study’ in Orange County
Also announced this week in California was the award of a 20MW / 80MWh battery storage project by development company Hecate Grid to technology provider Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems Americas (MHPS).
Hecate Grid, a joint venture to develop, own and operate energy storage systems formed by developer Hecate Energy and investor InfraRed Capital Partners, has contracted MHPS to supply full design and turnkey engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) services for Johanna Energy Storage System (ESS), in Santa Ana, Orange County, California. The project will actually be split across two systems at nearby locations.
MHPS will provide the complete BESS solution including battery management system (BMS) and energy dispatch management system for the project, using lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries. The company will also service the project under a 10-year service agreement. The Johanna ESS will be used in a “multi-year study” to determine whether growing demand for electricity in Orange County can be offset using clean, distributed energy on the CAISO grid.
Hecate Grid is entering into long-term contracts with an electric utility and a community choice aggregator (CCA) for the system’s use. Johanna ESS is scheduled to come online by the end of this year.