A total of 5,200MWh of battery energy storage systems (BESS) has been submitted to Australia’s Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation (EPBC) Act.
This includes two proposals from X-Elio Australia and BID Energy Partners, featuring a 300MW/1,200MWh BESS and a 1,000MW/4,000MWh BESS, both located in New South Wales.
The EPBC Act, administered by the federal government, aims to protect nationally threatened species and ecological communities. The approval must be received before a project can be developed.
If a BESS project is deemed to significantly impact these matters, it becomes a “controlled action” requiring assessment and approval under the EPBC Act. In contrast, if a BESS does not have a significant impact, it becomes “not a controlled action,” meaning it is clear for development.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
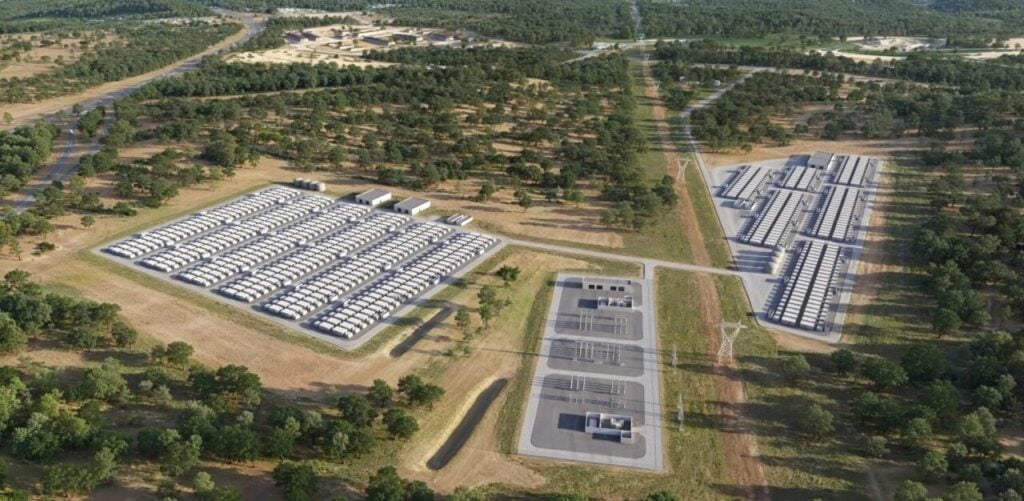
BID Energy’s 4,000MWh BESS in New South Wales
BID Energy, an independent advisory and development firm specialising in renewable energy projects, is leading the largest of the two initiatives.
The company is also pursuing another BESS project in Australia: the 400MW/800MWh Derringullen Energy Storage System near Yass, New South Wales.
The new utility-scale 4,000MWh Kiar BESS will be located in the Central Coast region of New South Wales, just under 100km north of Sydney. The project will connect to the National Electricity Market (NEM) via a 330kV transmission line running through the site, owned by network operator Transgrid.
By leveraging this existing infrastructure, BID Energy aims to minimise the costs of connecting the project to the NEM.
The Kiar BESS will include rows of enclosed battery modules connected to power conversion systems (PCS) and underground 33kV high-voltage ring main reticulation equipment and switchgear.
The layout and quantity of battery modules, PCS, and ring main units will be finalised during the detailed design and Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) process.
The project will cover approximately 110 hectares and will be decommissioned at the end of its proposed 25-year operational life. Construction is expected to take 18 to 24 months, with commissioning anticipated for late 2027 or early 2028.
BID Energy has committed to working with the Central Coast Council, local residents, Indigenous groups, businesses, and other stakeholders to ensure the project benefits the community through benefit-sharing arrangements.
X-Elio’s 1,200MWh BESS in the Southern Tablelands
Spanish sustainable energy developer X-Elio, owned by Canadian asset manager Brookfield, is proposing the 300MW/1,200MWh Canyonleigh BESS in the Southern Tablelands region of New South Wales.
The project is located near Brayton, around 200km southwest of Sydney and 120km northeast of Canberra.
The Canyonleigh BESS will be situated to the east of X-Elio’s proposed Willavale Park Renewable Energy project, which features 300MW/600MWh of BESS co-located with a 72MWp solar PV power plant. Like BID Energy’s Kiar BESS, the Canyonleigh system will connect to the NEM.
The project will cover approximately 48 hectares, with the BESS itself requiring around 13 hectares.
According to the EPBC Act application, the Canyonleigh BESS will consist of lithium-ion battery units housed in shipping container-style enclosures, along with inverters, transformers, and other related electrical infrastructure.
Construction, including grid connection and commissioning, is expected to take 12 to 18 months. The BESS will have an operational lifespan of between 20 and 30 years.
X-Elio’s expanding BESS Portfolio in Australia
X-Elio is actively developing energy storage projects across Australia, many of which integrate BESS with renewable energy generation, such as utility-scale solar PV.
Earlier this year, the company submitted plans for a 720MW solar-plus-storage project in Queensland to the EPBC Act. This project features a 4-hour duration 720MW/2,880MWh BESS.
In 2022, X-Elio’s 200MW Blue Grass Solar Farm near Chinchilla, Queensland, began operations. The project is set to add a cumulative 148MW grid-forming BESS in two stages.
The first stage, involving a 60MW BESS, is expected to reach mechanical completion by the third quarter of this year.
Our publisher, Solar Media, will host the Battery Asset Management Summit Australia 2025 on 26-27 August in Sydney. You can get 20% off your ticket using the code ESN20 at checkout.