China deployed 533.3MW of new electrochemical energy storage projects in the first three quarters of 2020, an increase of 157% on the same period in 2019.
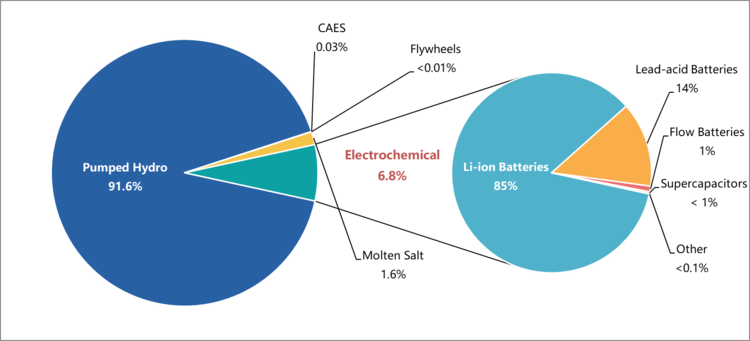
According to work by the China Energy Storage Alliance’s (CNESA) in-house research group, the country now has around 33.1GW of installed energy storage project capacity in total, with global cumulative capacity now at about 186.1GW. These figures include all forms of energy storage including pumped hydro, which still accounts for more than 90% of installed capacity.
Enjoy 12 months of exclusive analysis
- Regular insight and analysis of the industry’s biggest developments
- In-depth interviews with the industry’s leading figures
- Annual digital subscription to the PV Tech Power journal
- Discounts on Solar Media’s portfolio of events, in-person and virtual
However, pumped hydro’s share is being eroded steadily while electrochemical energy storage capacities’ share increases. In China, lithium-ion batteries make up about 85% of this electrochemical storage capacity and worldwide the figure is even higher, at 90%, CNESA’s ES Research found.
Worldwide, sodium sulfur (NAS) batteries take the next biggest share, at 5%, with lead-acid at about 4%. In China, the picture is slightly different, with lead-acid taking a 14% share, while sodium-sulfur – the only global manufacturer of which is Japan’s NGK Insulators, not even registering. In both pictures, flow batteries remain at about 1% and supercapacitors even less than that.
CNESA noted that during the third quarter, China’s installed capacity of electrochemical storage went beyond the 2GW mark, with 2242.92MW installed to date, against a global total of 10,902.4MW. For the period between January and September this year, 1,381.9MW of electrochemical storage was deployed worldwide, an increase of 42% on the same period last year, with the aforementioned 533.3MW in China.
According to CNESA’s research team therefore, 38% of global new energy storage capacity addition was in China, making it the world’s leader for the year so far. In addition to the significant ramp-up in capacity, CNESA’s monthly market update reported several significant steps forward in China alongside some major project news.
The country’s National Energy Administration (NEA) has recently also published a list of operational energy storage projects that have been selected as science and technology innovation pilot demonstration projects. Eight projects have been selected in five different provinces of China, following a two-year selection process.
Projects must have been in operation since the beginning of 2018 and in operation continuously for at least one year. All of them are lithium-ion battery-based, except for one which combines lithium-ion and flow batteries. Each of the projects had to cost at least RMB30 million (US$45.7 million) in investment.
The idea is that each will be exemplary of the value and benefits of energy storage in a different way, to build a comprehensive and representative picture of the industry. CNESA noted that the NEA has been keenly focused on promoting energy storage demonstration projects since the 2017 publication of the government’s ‘Guiding opinions on promoting energy storage technology and industry development’ document.
| Province | Description | Technology type | Energy storage application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qinghai | 20MW supporting storage project for national PV power generation testing base, by Huanghe hydropower development Co.,Ltd. | Lithium-ion battery, flow battery | Renewables generation-side |
| Hebei | Expanded national wind-PV-storage demonstration project, Phase II | Lithium-ion battery | Renewables generation-side |
| Fujian | Microgrid storage project, by CATL | Lithium-ion battery | Behind-the-meter |
| Jiangsu | 32MW storage project in Zhangjiagang city, by Conch group | Lithium-ion battery | Behind-the-meter |
| Jiangsu | 110.88MW / 193.6MWh storage project in Kunshan, Suzhou city | Lithium-ion battery | Grid-side |
| Fujian | 100MWh storage pilot demonstration project in Jinjiang city | Lithium-ion battery | Grid-side |
| Guangdong | 30MW storage ancillary frequency control project(Xiaomo power plant in Haifeng city), by Clou-CR Power | Lithium-ion battery | Supporting conventional thermal power to provide ancillary service |
| Guangdong | Storage frequency control project for Desheng power plant, in Foshan city | Lithium-ion battery | Supporting conventional thermal power to provide ancillary service |
In other industry news included in CNESA’s update, State Grid Hunan Comprehensive Energy Service has issued a tender for engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) partners to four renewable energy-plus-storage projects in four cities in Hunan province. State Grid Hunan Comprehensive Energy Service is a joint venture (JV) of state-owned power provider State Grid Hunan Electric Power Company and State Grid Comprehensive Energy Group.
The four contracts are for 22.5MW / 45MWh of energy storage capacity in Chenzhou, 7.5MW / 15MWh in Loudi, 20MW / 40MWh in Yongzhou and 10MW / 20MWh in Shaoyang, with a total combined capacity of 60MW / 120MWh. The JV will invest in projects to a maximum total price of RMB6.79 million.
Finally, CNESA also reported that during November, a 32MW / 64MWh lithium-ion battery energy storage project went online, making it China’s first-ever “independent commercial energy storage station”. The grid-connected project reduces curtailment of local solar and wind power and is in Golmud, Qinghai province. CNESA said that this is the first phase of the project.
Called the Shanghai Electric Golmud Meiman Minhang energy storage station, the battery system was provided by Shanghai Electric Gotion New Energy Technology and the EPC partner was Shanghai Electric New Energy. Described by CNESA as an “innovative pilot for the promotion of greater renewable energy penetration,” the project is shared by multiple owners of renewable energy generation facilities and is aimed at increasing their return on investment in those facilities.