During the opening address of Energy Storage Summit Latin America 2025, in Santiago, Chile, the Chilean Minister of Energy Diego Pardow Lorenzo said the country was most likely set to surpass its 2050 targets in 2027.
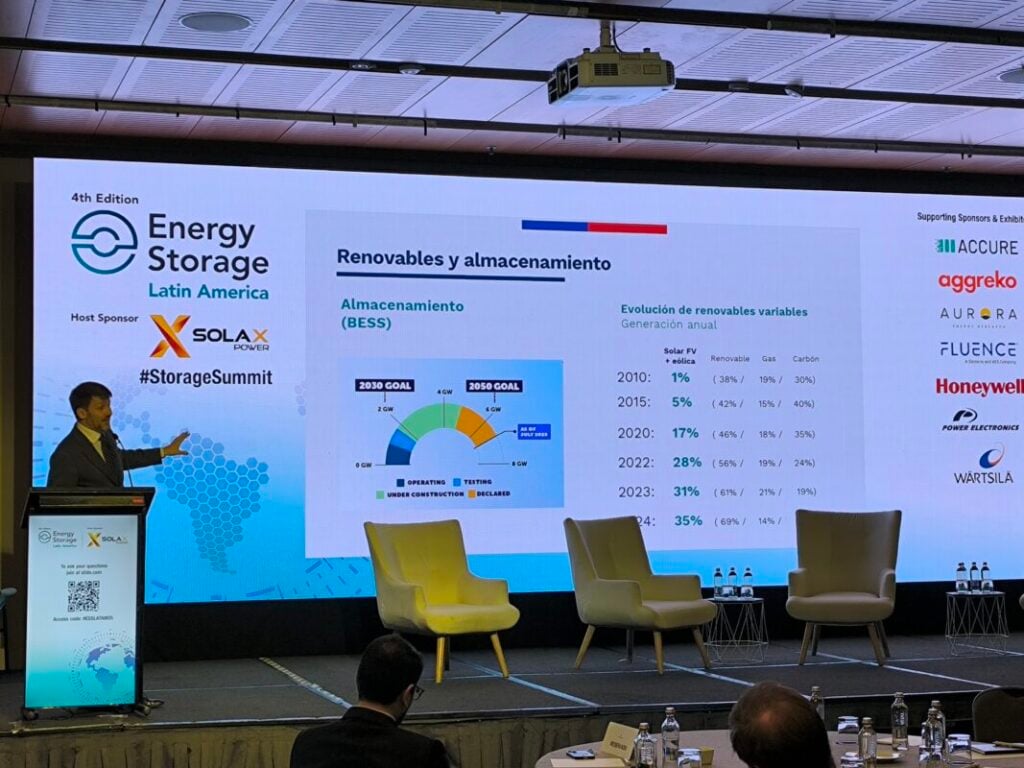
Pardow added that by January, Chile will have installed 2GW of battery energy storage systems (BESS), which represents the target set by 2030 for the country.
Moreover, the energy minister added that there are 8GW under construction, 2GW more than the 2050 target set by the government.
These numbers show the rapid expansion and construction of BESS projects in the country, one of the key takeaways of the conference’s first day.
Try Premium for just $1
- Full premium access for the first month at only $1
- Converts to an annual rate after 30 days unless cancelled
- Cancel anytime during the trial period
Premium Benefits
- Expert industry analysis and interviews
- Digital access to PV Tech Power journal
- Exclusive event discounts
Or get the full Premium subscription right away
Or continue reading this article for free
“What does that mean in terms of mobilising investment? Basically, each gigawatt of storage represents US$1 billion, which means we’ve already mobilised US$2 billion and are mobilising US$8 billion.”
Moreover, the integration of operational capacity in Chile has already shown how it already impacted the marginal costs in the country, added Pardow. The minister showed a chart (see below) comparing the prices between the first quarter of 2023 and 2025, were the prices during peak hours and even during the night have decreased from peaks of nearly US$200/MWh to highs of US$100/MWh. A twofold decrease.
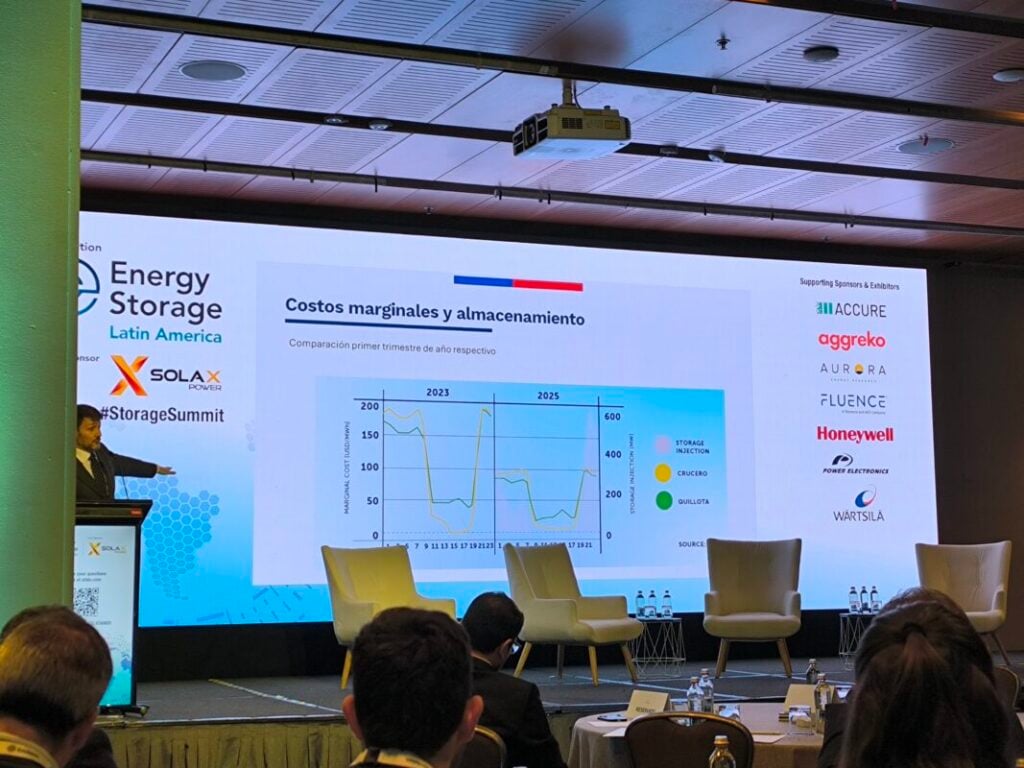
“What happens is that we no longer have blocks of oversupply. And we no longer have marginal costs at a price of zero, during the daylight hours. More importantly, the maximum costs outside of the daylight hours have been reduced by half.”
Pardow concluded that the challenge for the future lies in long-duration energy storage (LDES), which presents different challenges compared to short-term storage. Pardow gave the example of pumping hydro energy storage (PHES) stations, adding that these are different in Chile compared to other markets, in that those in Chile are located near the sea, in both the northern and central regions of the country.
“It is not exactly the same pumping stations that have flourished in China or during the 20th century in the US. Therefore, we will need to adapt. The outlook, once again, is promising. The outlook is auspicious, but the challenge ahead is similar to the one we’ve already faced,” said Pardow, referring to the learning curve made with short-term duration storage.